Difference between revisions of "IONI power supply schemes"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(Created page with "{| class="wikitable" |- ! Scheme !! Description !! Pros !! Cons |- | 300px|| Two switching power supplies, one high power voltage supply for mot...") |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|- | |- | ||
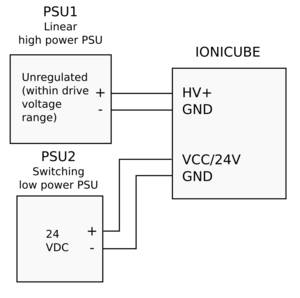
| [[File:ioni_psu_linear.png.png|300px]] || Linear (transformer based unregulated) power supply is used for motor supply and low power switching PSU for logic power. || | | [[File:ioni_psu_linear.png.png|300px]] || Linear (transformer based unregulated) power supply is used for motor supply and low power switching PSU for logic power. || | ||
| + | *Fault tolerant | ||
*No need for diodes | *No need for diodes | ||
*Linear PSU peak power handling | *Linear PSU peak power handling | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 3 December 2015
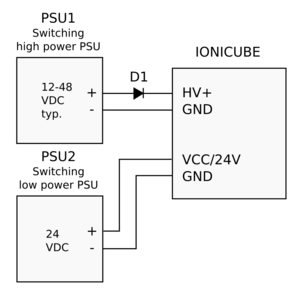
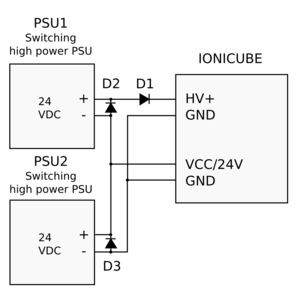
Diodes D1-D3 are typical silicon or schottky rectifier diodes that are sufficiently rated to carry the present voltages and currents. As diodes are inexpensive, there is no need to avoid oversizing them. Examples diodes:
- Diodes Inc. 10A02-T (10A 100V, leaded)
- Diodes Inc. 10A04-T (10A 400V, leaded)
- Fairchild FFPF30UP20STU (30A, 200V, leaded, isolated TO-220 case)
- Fairchild RURG3060 (30A 600V, leaded, non-isolated case - cooling tab is either anode or cathode)
- Fairchild STPS20120D (20A 120V, leaded, non-isolated case - cooling tab is either anode or cathode)