Difference between revisions of "Motor compatibility guide"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Note B (current rating)== | ==Note B (current rating)== | ||
| − | Current is the component to produce torque on motor. Motor torque is directly proportional to torque generated | + | Current is the component to produce torque on motor. Motor torque is directly proportional to torque generated with equation T=I*K where T is torque, I is current and K is the torque constant of motor (motor specific value, often defined in data sheet). |
| + | |||
| + | If drive is unable to drive (or is set deliberately to limit current) below motor ratings, it will cause the obtainable peak torque to be reduced. The reduction is proportional to the current reduction. For example, if motor is rated for 30A and drive can supply 20A, then torque is reduced by ratio 20/30 thus maximum obtainable torque is 67% of motor maximum rating. | ||
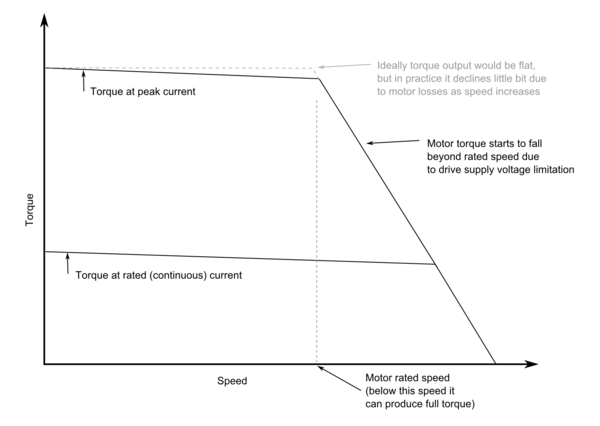
| + | {{picturebox|motorcurves_rated.png|600px|caption=Example of motor torque vs speed ratings at their specified currents and voltages}} | ||
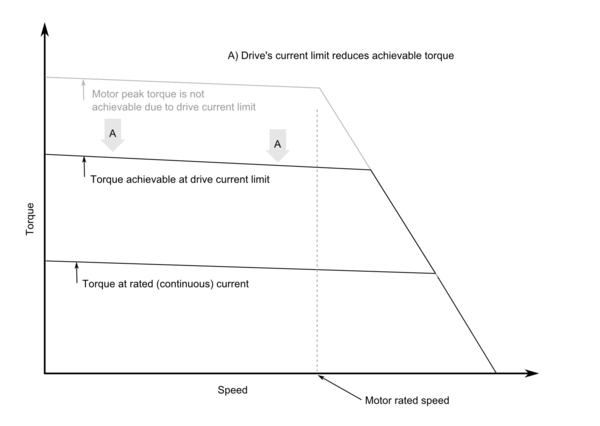
| + | {{picturebox|motorcurves_currentlimited.png|600px|caption=Example of motor torque vs speed ratings with drive that limits the torque output below motor spec}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{tip|In many practical machines, maximum torque is not required which makes even undersized drive suitable. Drive or motor will not have any reliability issues by that mismatch.}} | ||
| + | |||
==Note C (voltage rating)== | ==Note C (voltage rating)== | ||
==Note D (stepping motor feedback)== | ==Note D (stepping motor feedback)== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Argon_user_guide]] | [[Category:Argon_user_guide]] | ||
[[Category:IONI_user_guide]] | [[Category:IONI_user_guide]] | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 28 January 2016
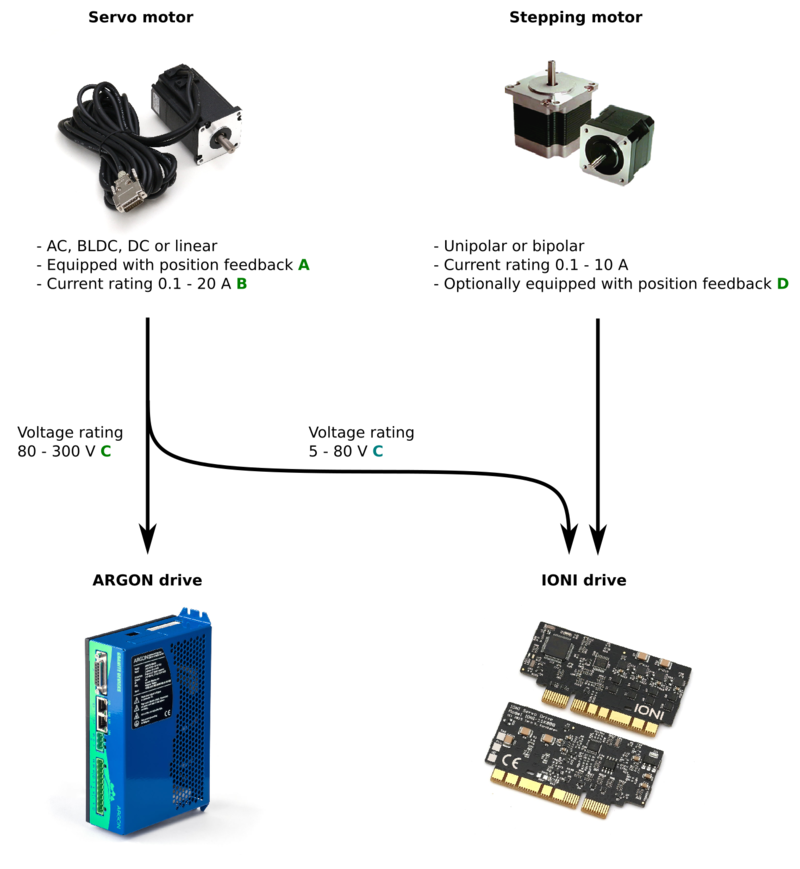
This page guides through matching the Granite Devices drive and various kinds of servo and stepping motors.
Contents
Overview
Note A (position feedback device)
Servo motor requires a position feedback device to operate with servo drive. It is recommended to have a position sensor that has resolution of at least 1000 increments (a.k.a. counts) per revolution. The higher the resolution, the better servo stiffness can be achieved.
Feedback device type must be one of the supported types. Following types are supported by different drive models:
- ARGON
- Incremental quadrature encoder
- Resolver (with separately available Argon resolver adapter)
- More than 99% of encoders are directly compatible, for technical details of compatible types see ARGON motor compatibility page.
- IONI
- Incremental quadrature encoder
- SinCos encoder
- More than 99% of encoders are directly compatible, for technical details of compatible types see IONI motor compatibility page.
About Hall sensors
Many AC/BLDC motors come also with Hall sensors. Hall sensors are supported by ARGON & IONI drives but these are not required for operation and can be left unconnected. Connecting & enabling Hall sensor can be used to speed up motor initialization at power-on. For more info, see Phasing a.k.a. phase search.
Unsupported feedback devices
Feedback devices that are not listed as supported, can be assumed to be unsupported and unsuitable. Examples of such types are:
- Tachogenerator/tachometer
- Serial data encoders (BiSS, SSI, EnDat etc)
In case of unsupported type, motor can be usually made compatibly by installing a compatible encoder in it. Compatible encoders are widely available in may sizes and fit most motors in the market. See list of compatible feedback devices.
Note B (current rating)
Current is the component to produce torque on motor. Motor torque is directly proportional to torque generated with equation T=I*K where T is torque, I is current and K is the torque constant of motor (motor specific value, often defined in data sheet).
If drive is unable to drive (or is set deliberately to limit current) below motor ratings, it will cause the obtainable peak torque to be reduced. The reduction is proportional to the current reduction. For example, if motor is rated for 30A and drive can supply 20A, then torque is reduced by ratio 20/30 thus maximum obtainable torque is 67% of motor maximum rating.
| In many practical machines, maximum torque is not required which makes even undersized drive suitable. Drive or motor will not have any reliability issues by that mismatch. |