Difference between revisions of "Determining motor pole count"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
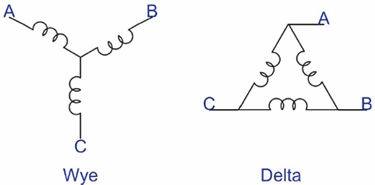
(Created page with "3 phase AC/BLDC motor winding schemes. A, B and C represent the phase wires coming out of motor. If magnetic pole count of permanent magnet AC/BLDC...") |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
#Rotate motor shaft by hand or tool and count the distinct snapping positions per one revolution. | #Rotate motor shaft by hand or tool and count the distinct snapping positions per one revolution. | ||
#Motor pole count is twice as much as the number of snapping positions found in the previous step. I.e. if motor snaps 2 times per revolution, it means that motor has 4 magnetic poles. | #Motor pole count is twice as much as the number of snapping positions found in the previous step. I.e. if motor snaps 2 times per revolution, it means that motor has 4 magnetic poles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tips: | ||
| + | *If motor is too stiff to rotate, reduce current. | ||
| + | *If snaps can't be felt, increase current to make them stronger. | ||
[[category:Troubleshooting]] | [[category:Troubleshooting]] | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 1 September 2013
If magnetic pole count of permanent magnet AC/BLDC motor is unknown, there is an easy way to determine it experimentally.
Needed items:
- 3 phase AC/BLDC motors
- Adjustable lab DC power supply
Procedure:
- Wire DC power supply + and - wires between any of two leads of the motor. I.e. + to A and - to B while C is not connected.
- Use the PSU to drive some DC current to the windings. Don't exceed motor's current rating. A good starting value may be 20-30% of motor continuous current. Now motor should start holding position as the rotor's magnets snap to the driven windings.
- Rotate motor shaft by hand or tool and count the distinct snapping positions per one revolution.
- Motor pole count is twice as much as the number of snapping positions found in the previous step. I.e. if motor snaps 2 times per revolution, it means that motor has 4 magnetic poles.
Tips:
- If motor is too stiff to rotate, reduce current.
- If snaps can't be felt, increase current to make them stronger.