Difference between revisions of "HV DC bus"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
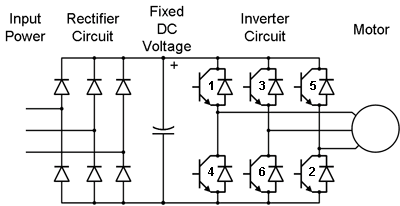
| − | [[File:Inverter.gif|thumb|A simplified typical motor drive high voltage circuity | + | [[File:Inverter.gif|thumb|A simplified typical motor drive high voltage circuity. <br/><br/>In this case the circuit has 3-phase AC input. 1-phase input is similar to this but only with four rectifier diodes instead of six.]] |
| + | HV DC bus refers to an internal high voltage DC supply bus of a motor drive. This voltage typically has voltage between 5 to 400 VDC depending on a drive model and is the source voltage to the power stage that actually drives current to motor windings. | ||
In [[Argon]] the HV DC bus is generated by rectified AC input voltage, so for example with 230 VAC input the DC but voltage becomes about 325 VDC. | In [[Argon]] the HV DC bus is generated by rectified AC input voltage, so for example with 230 VAC input the DC but voltage becomes about 325 VDC. | ||
| + | |||
| + | DC supplied drives, such as [[IONI]], [[VSD-E and VSD-XE]], do not have AC power input but direct HV DC input. | ||
[[category:glossary]] | [[category:glossary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 21 March 2015
HV DC bus refers to an internal high voltage DC supply bus of a motor drive. This voltage typically has voltage between 5 to 400 VDC depending on a drive model and is the source voltage to the power stage that actually drives current to motor windings.
In Argon the HV DC bus is generated by rectified AC input voltage, so for example with 230 VAC input the DC but voltage becomes about 325 VDC.
DC supplied drives, such as IONI, VSD-E and VSD-XE, do not have AC power input but direct HV DC input.