Difference between revisions of "Setpoint signal"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
m (Text replacement - "{{param|PWM}}" to "PWM") |
|||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
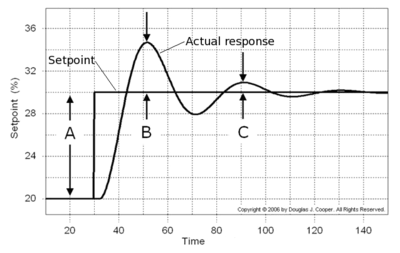
| − | + | [[File:Setpoint and actual.png|thumb|400px|An example setpoint signal (target value) and measured response signal (realized output value) of a control system.]] | |
| − | * Position | + | Setpoint (a.k.a reference) signal is a signal that will be used as ''target value'' in control systems. Typical occurrencies of setpoint signals in GD products are: |
| − | * | + | * Position setpoint |
| − | * Torque | + | * Velocity setpoint |
| − | I.e. position | + | * Torque setpoint |
| − | ==Physical | + | I.e. position setpoint value may be "1234" which could mean a target position of 1234 mm in some linear actuator. Or torque setpoint of 5.0 could mean that motor is asked to produce 5 Nm torque. |
| − | + | ==Physical setpoint signal types== | |
| − | * Analog | + | Setpont signals may have several representations in real world such as: |
| + | * [[Analog setpoint]] signal | ||
* [[Pulse and direction]] signals | * [[Pulse and direction]] signals | ||
* [[PWM]] signal | * [[PWM]] signal | ||
* Serial communication command | * Serial communication command | ||
| − | In these cases there will be a conversion between input and output units. For example when using +/-10V | + | In these cases there will be a conversion between input and output units. For example when using +/-10V as velocity setpoint, the relation between input to output types could be 1 Volt per 100 rpm (or any other scale). |
| + | ==Setpoint signal characteristics== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! !! [[Analog setpoint|Analog]] !! [[Pulse and direction|Pulse & dir]] or [[Quadrature]] !! [[PWM]] !! Serial / Network | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Scale & range || Absolute (limited) || Incremental (infinite) || Absolute (limited) || | ||
| + | *Absolute (near infinite) | ||
| + | *Incremental (infinite) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Setpoint uses in motion control || Torque, velocity || Position, velocity || Torque, velocity || Position, torque, velocity, parameters | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Pros | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | * Widely used | ||
| + | * Easy to measure | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *Widely used | ||
| + | *Exact | ||
| + | *Noise robust | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *EMI noise robust | ||
| + | *Precise | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *High resolution & accuracy | ||
| + | *Reduce wiring | ||
| + | *More functions than just setpoint | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Cons | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *EMI noise sensitive | ||
| + | *Offset & gain errors | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *Limited resolution at low frequency | ||
| + | *Need reference zeroing because incremental | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *Various "standards", sometimes incompatible | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | *Many standards | ||
| + | *Usually incompatible with other standards | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | [[Category:Signals]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Glossary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:59, 28 August 2015
Setpoint (a.k.a reference) signal is a signal that will be used as target value in control systems. Typical occurrencies of setpoint signals in GD products are:
- Position setpoint
- Velocity setpoint
- Torque setpoint
I.e. position setpoint value may be "1234" which could mean a target position of 1234 mm in some linear actuator. Or torque setpoint of 5.0 could mean that motor is asked to produce 5 Nm torque.
Physical setpoint signal types[edit | edit source]
Setpont signals may have several representations in real world such as:
- Analog setpoint signal
- Pulse and direction signals
- PWM signal
- Serial communication command
In these cases there will be a conversion between input and output units. For example when using +/-10V as velocity setpoint, the relation between input to output types could be 1 Volt per 100 rpm (or any other scale).
Setpoint signal characteristics[edit | edit source]
| Analog | Pulse & dir or Quadrature | PWM | Serial / Network | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale & range | Absolute (limited) | Incremental (infinite) | Absolute (limited) |
|
| Setpoint uses in motion control | Torque, velocity | Position, velocity | Torque, velocity | Position, torque, velocity, parameters |
| Pros |
|
|
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
|
|