Difference between revisions of "Tuning velocity controller"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Velocity controller tuning means finding the correct drive settings and feedback gain values to achieve a proper [[Servo stiffness]] and response to a velocity [[Setpoint signal|setpoint]] change. | Velocity controller tuning means finding the correct drive settings and feedback gain values to achieve a proper [[Servo stiffness]] and response to a velocity [[Setpoint signal|setpoint]] change. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 33: | ||
===Finding velocity control gain values=== | ===Finding velocity control gain values=== | ||
| + | {{tip|If the drive faults during this testing due to overcurrent, see [[Tuning torque controller]] for solutions. If drive faults due to following error or motion fault, increase the goal deviation fault limits at Fault limits tab.}} | ||
| + | ====Tuning protocol==== | ||
| + | Tuning is begun with low or medium target speeds (TSP1 & 2 values below 5000). | ||
[[File:Veltuning2.png|800px]] | [[File:Veltuning2.png|800px]] | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | Initial velocity response with the default settings. As seen from the achieved velocity graph, it follows the setpoint velocity lazily and exhibits [[overshooting]]. In such state motor [[servo stiffness]] is low can be easily decelerated by adding load to the shaft. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Veltuning4.png|800px]] | [[File:Veltuning4.png|800px]] | ||
| − | [[File: | + | |
| + | Begin tuning by increasing [[KVP]] gain. This makes motor follow velocty setpoint much better. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To try different gains, go to Tuning tab, change value and click the Apply settings button. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Veltuning3.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | When [[KVP]] has been increased too much, the system becomes unstable and may start oscillating. In such case, you may hit Esc button to disable drive, reduce the gain and enable drive again. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tip: torque bandwidth has significant effect on the behavior of KVP value and the point where it goes unstable. One may experiment different [[TBW]] settings to find the optimum. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Veltuning6.png|800px]] | [[File:Veltuning6.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once a maximum perfectly stable [[KVP]] value has been found, start increasing [[KVI]] gain by a similar fashion. The higher KVI value is, the better servo stiffness. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Veltuning5.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | If [[KVP]] is increased too much, the result is [[overshooting]] and even sustained oscillation. The cure is similar to the too high [[KVP]] gain as described earlier. | ||
[[File:velocitylowgain.png|800px]] | [[File:velocitylowgain.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once stable and stiff gains has been found, increase setpoint values (TSP1 & 2) to test the settings with higher speeds. If necessary adjust the gains experimentally to find the optimum tuning that works satisfactory on all needed speeds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advanced tuning: Feed-forwards==== | ||
| + | [[Feed-forward]] parameters may be used to boost motor responsiveness to setpoint change. Feed-forward gains [[VFF]] and [[AFF]] essentially compensate system friction and mass limiting the dynamic performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The recommended way to tune FF gains, is to start increasing velocity feed-forward [[VFF]] until the optimum level has been found. After that, increase acceleration feed-forward [[AFF]] until the optimum point has been reached. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:velocitylowgainff.png|800px]] | [[File:velocitylowgainff.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the image above a sharp response has been achieved even with low feedback gains as feed-forward gains help motor to accelerate as demanded. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:velocitystable.png|800px]] | [[File:velocitystable.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The image above shows similar response without feed-forwards but using high feedback gain values (optimally tuned according to the previous chapter). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Problem cases==== | ||
| + | In this test we run motor with higher speeds (TSPn > 10000) and illustrate few typical problem cases. | ||
| + | |||
[[File:currentsaturatin.png|800px]] | [[File:currentsaturatin.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The image above shows acceleration limited by insufficient torque produced by the motor. In this example the acceleration limit is set too high to be accelerated with the given motor torque limits (or current limits). | ||
| + | |||
| + | To verify if the problem happens due to torque limit, tick also Torque achieved and Torque setpoint signals from the Testing tab settings. In such way also motor currents will be displayed simultaneously with the position response curves. If the torque curve is limited to the set peak current limit [[MMC]], then the problem is insufficient torque. In the image above we can see that the torque curves are saturated/clipping at 5A and -5A levels which matches the configured [[MMC]] value of 5A in this demonstration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To help this, try: | ||
| + | *Increasing current limits [[MMC]] and [[MCC]] if possible | ||
| + | *Reducing acceleration [[CAL]] and/or velocity [[CVL]] limits | ||
[[File:velocityunstable.png|800px]] | [[File:velocityunstable.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The above example shows instability and oscillation with high speeds even when the system was stable at lower speeds with the same parameters. In such case tune the system again at the most infavourable conditions and speeds to achieve stability over all required operating conditions. | ||
===Steps to do after tuning finished=== | ===Steps to do after tuning finished=== | ||
Revision as of 22:43, 28 August 2013
Velocity controller tuning means finding the correct drive settings and feedback gain values to achieve a proper Servo stiffness and response to a velocity setpoint change.
This tuning guide is for you if the final application uses the motor in velocity control mode such as spindle or as position mode with external closed loop position controller such as EMC2.
Contents
Velocity control tuning method
| If motor has been tuned without the real load (i.e. motor shaft not attached), tuning parameters should be re-adjusted with the real load as the dynamic properties of the load has a significant effect on them. Large change of load properties may even cause servo instability. |
Preparations
Steps to do to begin position tuning:
- Ensure that motor is parameterized correctly and working and torque control tuning has been properly done.
- Attach motor to the target load and ensure it can rotate in both directions infinitely
- Make following parameter changes to Granity and click apply afterwards:
- Set drive in velocity control mode CM
- Choose Serial only setpoint input CM
- Make other necessary adjustments to have drive powered and enabled
- Untick Setpoint smoothing CIS
- Set Goals tab DIV and MUL to 50
- Set acceleration CAL & velocity CVL limits reasonably to the levels that motor is expected to handle
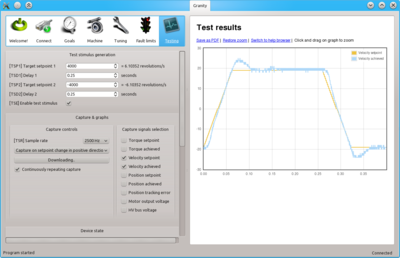
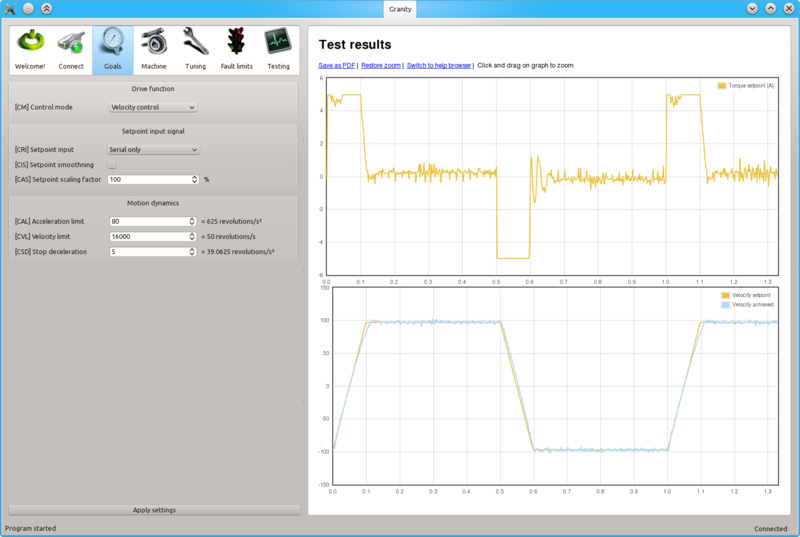
- Set-up the test stimulus and capture settings from Testing tab (an example, may be varied):
- Set target setpoint 1 TSP1 between 1000 and 16383 (16383 equals the max speed that is configured via CVL)
- Set delay 1 TSD1 to 0.25 seconds
- Set target setpoint 2 TSP2 to same, but negative, value of TSP1
- Set delay1 STD2 to 0.25 s
- Choose sample rate TSR of 500 to 2500 Hz
- Choose Capture setpoint change in positive direction from the dropdown
- Tick Continuously repeating capture
- Tick Velocity setpoint and Velocity achieved from signals
- Tick Start capture to begin continous capture.
- Tick Enable test stimulus TSE to begin a continuous position back and forth spinning motion generation
Once the steps above are done, motor should be generating direction reversing spinning and velocity response graphs should appear on the right side of Granity about once in 3-5 seconds.
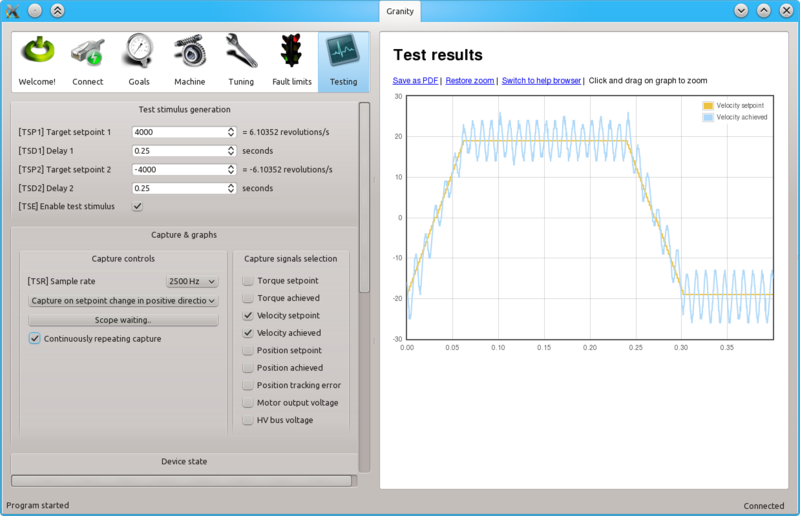
Finding velocity control gain values
| If the drive faults during this testing due to overcurrent, see Tuning torque controller for solutions. If drive faults due to following error or motion fault, increase the goal deviation fault limits at Fault limits tab. |
Tuning protocol
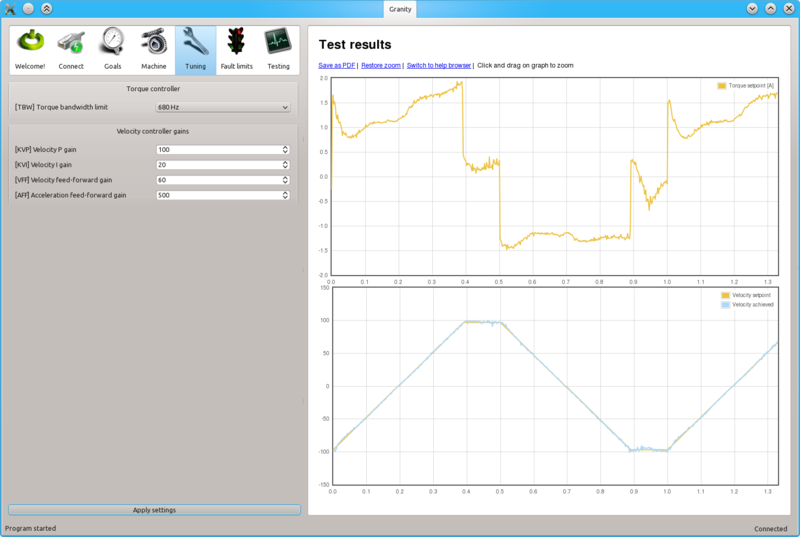
Tuning is begun with low or medium target speeds (TSP1 & 2 values below 5000).
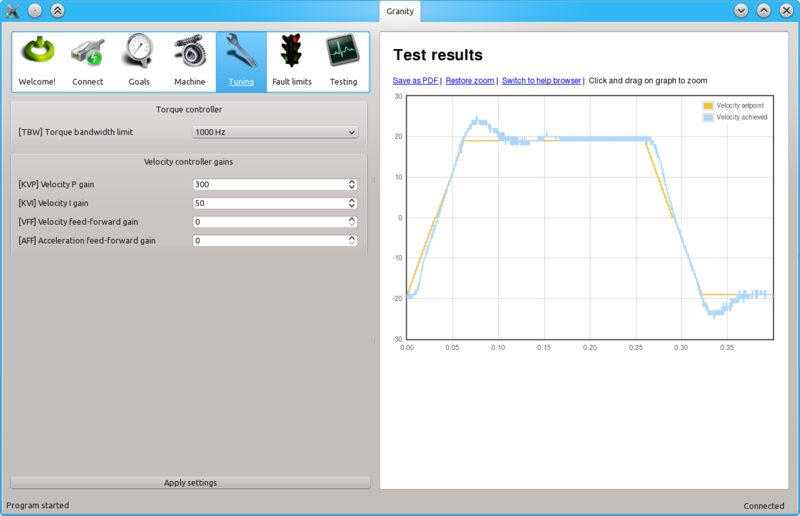
Initial velocity response with the default settings. As seen from the achieved velocity graph, it follows the setpoint velocity lazily and exhibits overshooting. In such state motor servo stiffness is low can be easily decelerated by adding load to the shaft.
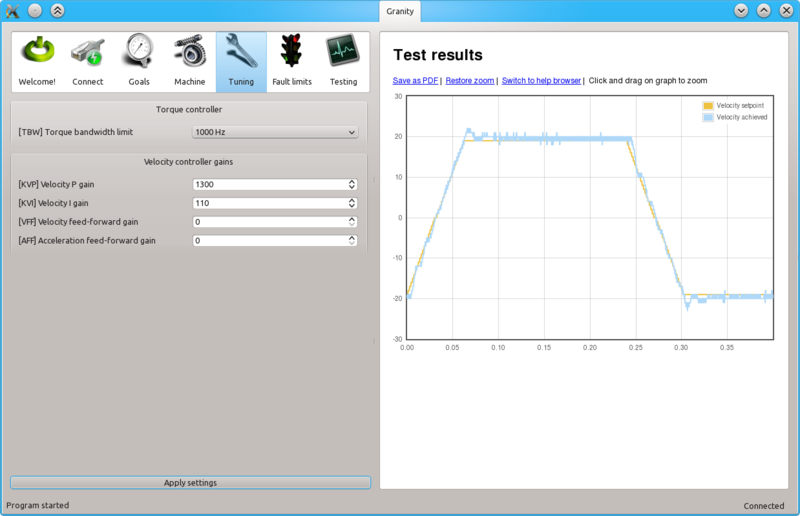
Begin tuning by increasing KVP gain. This makes motor follow velocty setpoint much better.
To try different gains, go to Tuning tab, change value and click the Apply settings button.
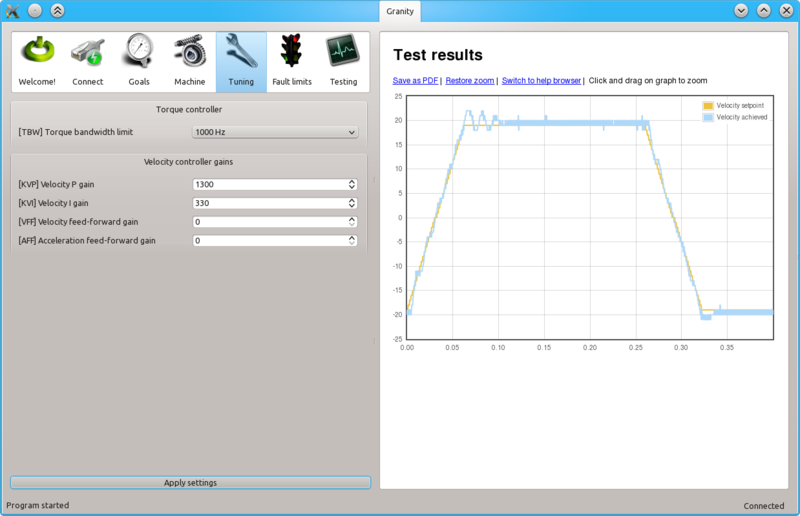
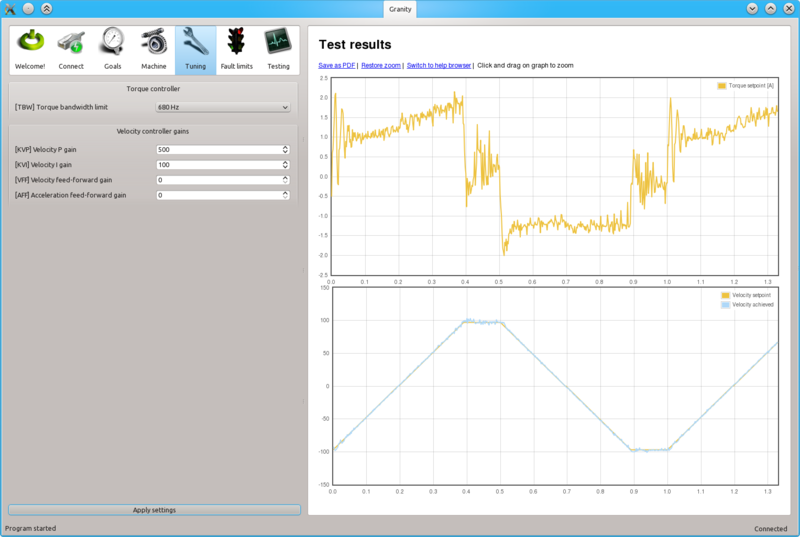
When KVP has been increased too much, the system becomes unstable and may start oscillating. In such case, you may hit Esc button to disable drive, reduce the gain and enable drive again.
Tip: torque bandwidth has significant effect on the behavior of KVP value and the point where it goes unstable. One may experiment different TBW settings to find the optimum.
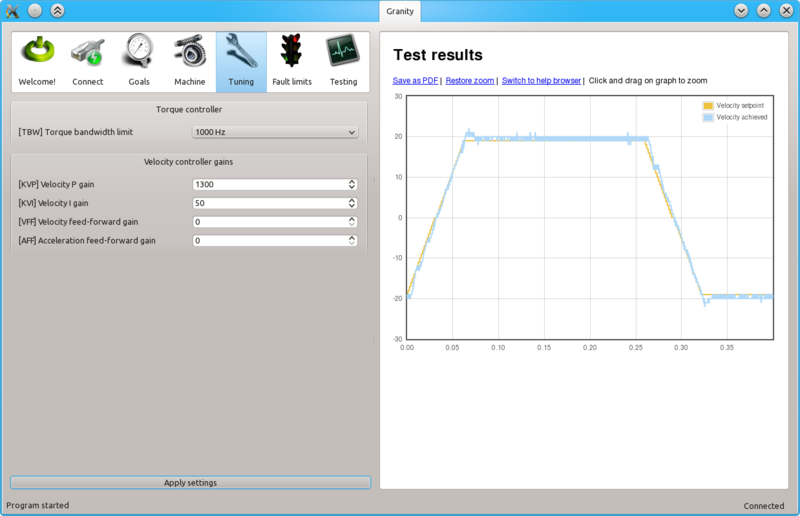
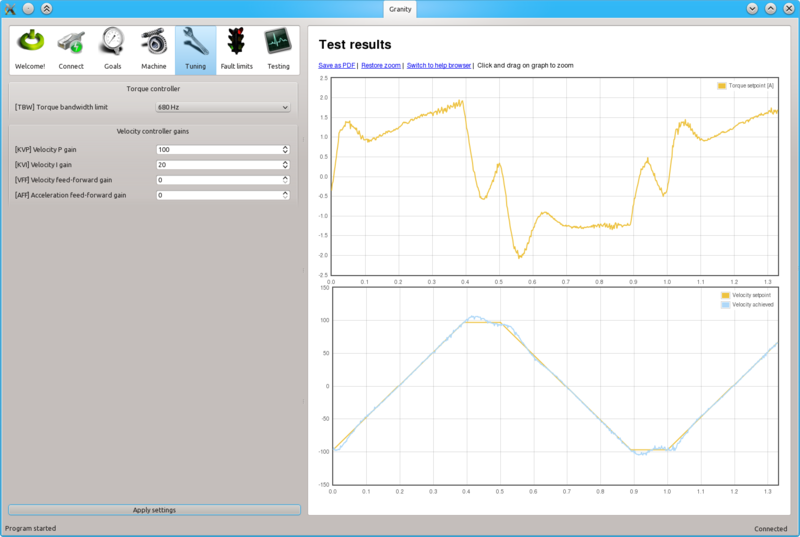
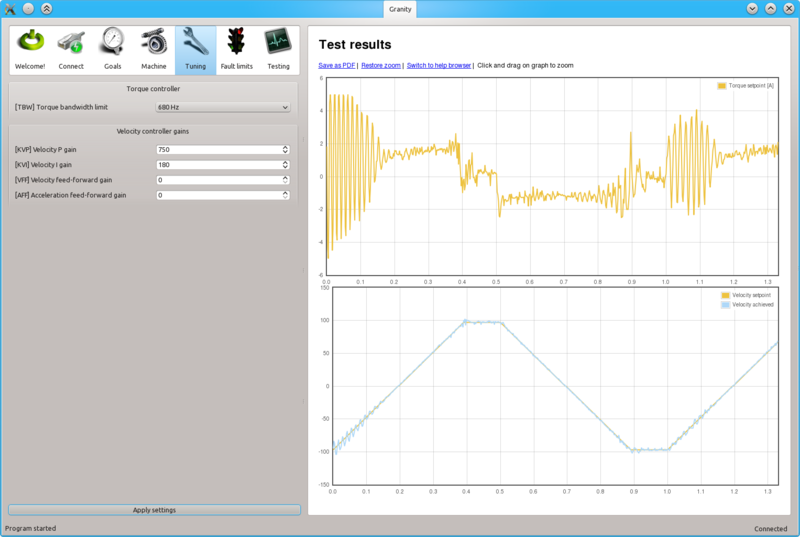
Once a maximum perfectly stable KVP value has been found, start increasing KVI gain by a similar fashion. The higher KVI value is, the better servo stiffness.
If KVP is increased too much, the result is overshooting and even sustained oscillation. The cure is similar to the too high KVP gain as described earlier.
Once stable and stiff gains has been found, increase setpoint values (TSP1 & 2) to test the settings with higher speeds. If necessary adjust the gains experimentally to find the optimum tuning that works satisfactory on all needed speeds.
Advanced tuning: Feed-forwards
Feed-forward parameters may be used to boost motor responsiveness to setpoint change. Feed-forward gains VFF and AFF essentially compensate system friction and mass limiting the dynamic performance.
The recommended way to tune FF gains, is to start increasing velocity feed-forward VFF until the optimum level has been found. After that, increase acceleration feed-forward AFF until the optimum point has been reached.
In the image above a sharp response has been achieved even with low feedback gains as feed-forward gains help motor to accelerate as demanded.
The image above shows similar response without feed-forwards but using high feedback gain values (optimally tuned according to the previous chapter).
Problem cases
In this test we run motor with higher speeds (TSPn > 10000) and illustrate few typical problem cases.
The image above shows acceleration limited by insufficient torque produced by the motor. In this example the acceleration limit is set too high to be accelerated with the given motor torque limits (or current limits).
To verify if the problem happens due to torque limit, tick also Torque achieved and Torque setpoint signals from the Testing tab settings. In such way also motor currents will be displayed simultaneously with the position response curves. If the torque curve is limited to the set peak current limit MMC, then the problem is insufficient torque. In the image above we can see that the torque curves are saturated/clipping at 5A and -5A levels which matches the configured MMC value of 5A in this demonstration.
To help this, try:
- Increasing current limits MMC and MCC if possible
- Reducing acceleration CAL and/or velocity CVL limits
The above example shows instability and oscillation with high speeds even when the system was stable at lower speeds with the same parameters. In such case tune the system again at the most infavourable conditions and speeds to achieve stability over all required operating conditions.
Steps to do after tuning finished
- Stop test stimulus by unticking TSE
- Stop scope catpure by unticking Continuously repeating capture
- Undo all temporary changes made to settings
- Save settings to drive memory by clicking Save settings on drive non-volatile memory button
- Set preferred setpoint source CRI, also consider the use of CIS
- If setpoint signal scaling is needed, adjust MUL and DIV values
| If drive will be controlled by an external motion controller with acceleration & velocity limits, such as CNC controller programs like Mach3 or EMC2, then its recommended to increase acceleration limit CAL to the maximum value of 32767 and disable setpoint smoothing CIS to prevent drive's internal acceleration limiter modifying the setpoint signal. Using these settings effectively disables the internal acceleration limit and let's external controller to control accelerations. |