Difference between revisions of "Argon resolver adapter"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
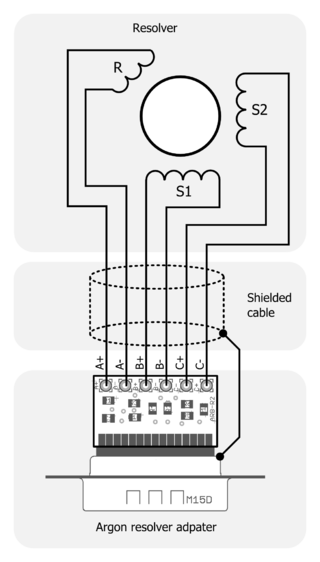
[[File:Resolveradapterwiring.png|thumb|320px|Connection of resolver to adapter.]] | [[File:Resolveradapterwiring.png|thumb|320px|Connection of resolver to adapter.]] | ||
| − | Resolver has total of 6 wires and 3 windings: one for rotor (primary) and two stators (secondaries). Rotor connects to the adapter pins A+ and A- while secondaries connect to B+/- and C+/-. | + | Resolver has total of 6 wires and 3 windings: one for rotor (primary) and two stators (secondaries). Rotor connects to the adapter pins A+ and A- while secondaries connect to B+/- and C+/-. A shielded cable is required and shield should be connected to D-sub connector frame to reduce [[EMI]] noise. |
If pin-out of resolver is unknown, it can be found out with multimeter by finding the wire pairs where coils are connected. Rotor can be identified by searching for lowest resistance coil. Stators typically have at least twice as high resistance compared to rotor. | If pin-out of resolver is unknown, it can be found out with multimeter by finding the wire pairs where coils are connected. Rotor can be identified by searching for lowest resistance coil. Stators typically have at least twice as high resistance compared to rotor. | ||
[[category:Motor drives]] | [[category:Motor drives]] | ||
[[category:Argon]] | [[category:Argon]] | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 28 March 2014
Argon resolver adapter is a small sized adapter device that adds resolver feedback device support to Argon servo drive.
Usage
Resolver has total of 6 wires and 3 windings: one for rotor (primary) and two stators (secondaries). Rotor connects to the adapter pins A+ and A- while secondaries connect to B+/- and C+/-. A shielded cable is required and shield should be connected to D-sub connector frame to reduce EMI noise.
If pin-out of resolver is unknown, it can be found out with multimeter by finding the wire pairs where coils are connected. Rotor can be identified by searching for lowest resistance coil. Stators typically have at least twice as high resistance compared to rotor.