Difference between revisions of "Signal path of motor drive"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(→Setpoint signal path) |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
[[Category:Development]] | [[Category:Development]] | ||
==Setpoint scale examples== | ==Setpoint scale examples== | ||
| + | Assuming control cycle to be 400µs / 2500 Hz (default in GD drives). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example 1=== | ||
| + | *Motor has 2500 P/R encoder (10000 CPR) and user wants to rotate it at 1000 rpm when scaling is set to 1:1 (MUL/DIV=1) | ||
| + | *Rotation speed is 1000/60 = 16.667 revs/s (RPS) Needed encoder count frequency is 16.667*10000 = 16667 counts/s. | ||
| + | *Internal setpoint is the amount of counts per control cycle so in this case it's 16667/2500 = 66.667 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because set point is integer value user must round setpoint to 66 or 67. To achieve exact speed, he could change input scaling (MUL/DIV) to allow unrounded value here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Acceleration and velocity limits | ||
| + | If DIV is 50, then user must have [[CVL]] value at least 3333 (66.6667*50). | ||
| + | |||
| + | If user wants motor to accelerate to 1000 rpm in 0.1 seconds, then [[CAL]] is value should be 3333/2500/0.1 = 13.33. Value must be again rounded to integer and rounding error could be reduced by adjusting scaling (adjust DIV). | ||
Revision as of 13:58, 7 April 2014
In Granite Devices drives the torque, velocity and position limits and setpoints are defined as integer numbers. The vales are represented "hardware" scale which are described below.
Contents
Setpoint signal path
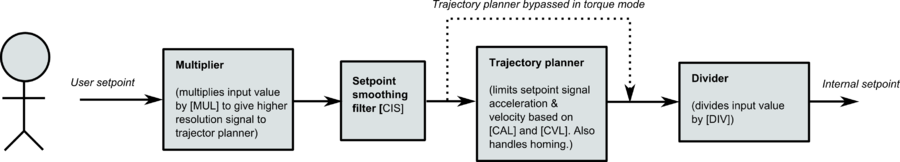
Setpoint signal path converts user setpoint to internal setpoint.
Setpoint signal path
Main parts are:
- Input multiplier. Purpose of this is to increase resolution of input setpoint to allow more fine grained velocity & acceleration control in trajectory planner. By default MUL value is 50.
- Setpoint smoothing filter. If enabled, applies low pass filter to signal reducing jitter and roughness of signal but also introduces about some delay. By default the filter has 100% attenuation at 250Hz.
- Trajectory planner. This limits rate of change of setpoint signal based on CVL and CAL parameters. Output rate maximum rate of change:
- Velocity changes max CAL nubmer of units per control cycle (control cycle is 400µs in most GD drives)
- Velocity maximum value is limited to CVL
- Input divider. This divides setpoint signal by DIV to give desired output scale for internal setpoint. Combination of multiplier and divider can be used change total scaling of setpoint signal.
Setpoint source scales
Different setpoint sources have different range and scale:
| Setpoint source | Type | Range | Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse & directon | Incremental | Infinite |
|
| Quadrature | Incremental | Infinite |
|
| PWM | Absolute | Full input scale equals setpoint range of +/-16384 | Direct 1:1 absolute value in all modes |
| Analog | Absolute | Full input scale equals setpoint range of +/-16384 | Direct 1:1 absolute value in all modes |
| Serial (SimpleMotion V2) | Absolute & incremental | Infinite | Direct 1:1 absolute value in all modes |
It should be noted that trajectory planner operates after multiplier meaning that CVL velocity limit value is not in equal scale with velocity setpoint value.
Internal setpoint
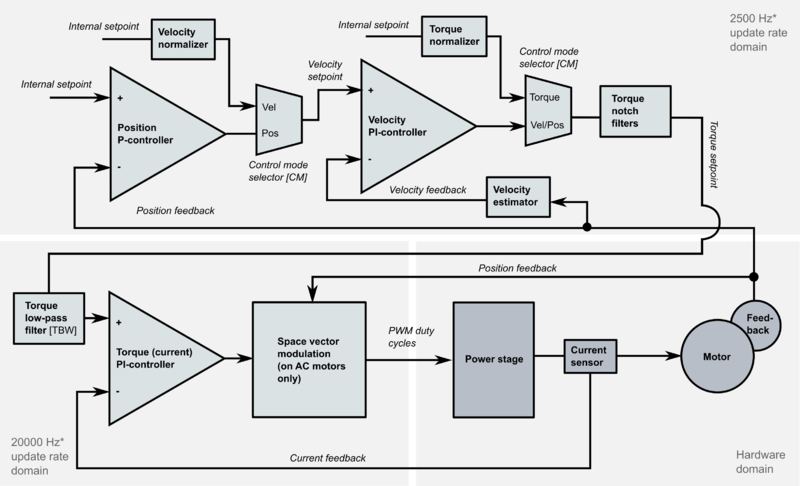
Internal setpoint equals the setpoint and feedback scale of signals in the controller (see below). The scale of feedback signals are:
- Position feedback: position sensor counter raw value
- Velocity feedback: number of feedback device counts per one control cycle. Obtained by calculating the difference of position feedback values at every control cycle.
- Torque: hardware specific scale, however Torque scaler knows the hardware scale and scales internal setpoint so that value of +/-16384 represents full torque scale (i.e. internal setpoint value 16384 outputs configured peak current MMC and 8192 outputs MMC/2)
Controller
The default controller type of GD drives is cascaded type where each controlled variable has it's own PI or P controller. In position mode such structure is called as PIV controller.
Setpoint scale examples
Assuming control cycle to be 400µs / 2500 Hz (default in GD drives).
Example 1
- Motor has 2500 P/R encoder (10000 CPR) and user wants to rotate it at 1000 rpm when scaling is set to 1:1 (MUL/DIV=1)
- Rotation speed is 1000/60 = 16.667 revs/s (RPS) Needed encoder count frequency is 16.667*10000 = 16667 counts/s.
- Internal setpoint is the amount of counts per control cycle so in this case it's 16667/2500 = 66.667
Because set point is integer value user must round setpoint to 66 or 67. To achieve exact speed, he could change input scaling (MUL/DIV) to allow unrounded value here.
- Acceleration and velocity limits
If DIV is 50, then user must have CVL value at least 3333 (66.6667*50).
If user wants motor to accelerate to 1000 rpm in 0.1 seconds, then CAL is value should be 3333/2500/0.1 = 13.33. Value must be again rounded to integer and rounding error could be reduced by adjusting scaling (adjust DIV).