Difference between revisions of "Overshooting"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:High accuracy settling time measurements figure 1.png|thumb]] | [[File:High accuracy settling time measurements figure 1.png|thumb]] | ||
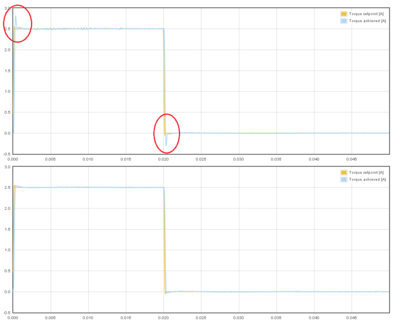
| − | [[File:Torque controller overshooting.png|thumb|A practical example of overshooting in torque control response. The spikes may trigger over current protection. By adjusting torque control gains (i.e. motor resistance & inductance parameters) solves this issue.]] | + | [[File:Torque controller overshooting.png|thumb|A practical example of overshooting in torque control response (top) and non-overshooting response (below). The spikes may trigger over current protection. By adjusting torque control gains (i.e. motor resistance & inductance parameters) solves this issue.]] |
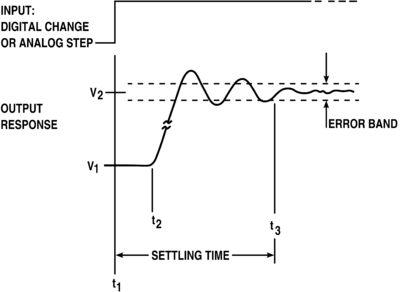
In control theory and electronics, overshoot is when a signal exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as servo systems. It is often followed by ringing that attenuates over time or keeps oscillating endlessly. | In control theory and electronics, overshoot is when a signal exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as servo systems. It is often followed by ringing that attenuates over time or keeps oscillating endlessly. | ||
See more on Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overshoot_(signal) Overshoot] | See more on Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overshoot_(signal) Overshoot] | ||
[[Category:Glossary]] | [[Category:Glossary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:59, 12 April 2015
In control theory and electronics, overshoot is when a signal exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as servo systems. It is often followed by ringing that attenuates over time or keeps oscillating endlessly.
See more on Wikipedia: Overshoot