IONI power supply schemes
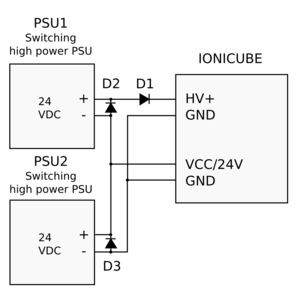
Diodes D1-D3 are typical silicon or schottky rectifier diodes that are sufficiently rated to carry the present voltages and currents. As diodes are inexpensive, there is no need to avoid oversizing them. Examples diodes:
- Diodes Inc. 10A02-T (10A 100V, leaded)
- Diodes Inc. 10A04-T (10A 400V, leaded)
- Fairchild FFPF30UP20STU (30A, 200V, leaded, isolated TO-220 case)
- Fairchild RURG3060 (30A 600V, leaded, non-isolated case - cooling tab is either anode or cathode)
- Fairchild STPS20120D (20A 120V, leaded, non-isolated case - cooling tab is either anode or cathode)
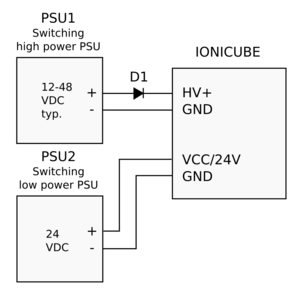
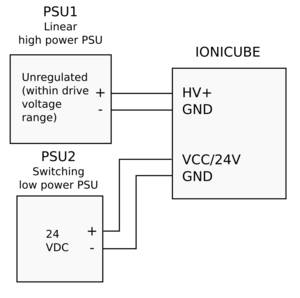
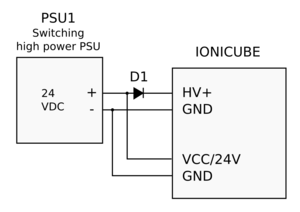
| Some switching power supplies can tolerate reversed current flow from drive to PSU (renegerative current). In case of such PSU, D1 may be omitted. If unsure about PSU behavior in regeneration, always add D1. |
| Leaded diodes may be easiest to install right at PSU terminals, no extra wiring needed. |
In no event the Product Information or parts hereof shall be regarded as guarantee of conditions or characteristics. The Product Information or any part thereof may also not be regarded as a warranty of any kind. No liability of any kind shall be assumed by Author with respect to Product Information or any use made by you thereof, nor shall Author indemnify you against or be liable for any third party claims with respect to such information or any use thereof.
As content of this Wiki may be edited by user community, Granite Devices Oy or it's affiliates do not take any responsibility of the contents of this Wiki. Use information at your own risk. However, Granite Devices staff attempts to review all changes made to this Wiki and keep information trustworthy.
Without written consent, Granite Devices' Products or Intellectual Property shall not be used in situations or installations where living beings, material property, or immaterial property could be harmed by the operation, features or failures of Product. Products may only be used in a way where hazards like moving parts, electric shock, laser radiation, or fire can't be realized even if the content of this Wiki would suggest otherwise.