Difference between revisions of "Granity user guide/Fault limits"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(→Drive fault limits) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{SetGranityTabPageTitle|Fault limits}}[[File:GranityFaultlimits.png|thumb]] |
| − | * Set fault triggering levels | + | This tab serves as: |
| + | * Set fault triggering levels and tolerances | ||
==Parameters== | ==Parameters== | ||
| − | === | + | ===Drive fault limits=== |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! Short [[GUI]] name !! [[GUI]] name !! Description !! How to use | |
| − | + | |- | |
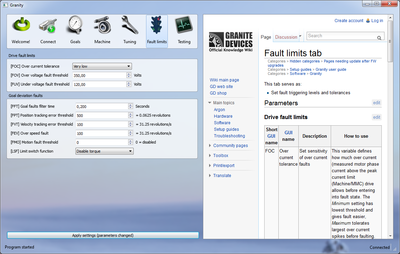
| + | | FOC || Over current tolerance || Set sensitivity of over current faults || This variable defines how much over current (measured motor phase current above the peak current limit (Machine/MMC) drive allows before entering into fault state. The ''Minimum'' setting has lowest threshold and gives fault easier, ''Maximum'' tolerates largest over current spikes before faulting. | ||
| + | Set this as low as possible without getting OC faults in normal use to maximally protect your equipment. If larger than ''Medium'' setting is needed, see [[Over current fault troubleshooting]] for solution to the problem. | ||
| − | [[ | + | FOC is firmware specific, it adjust including, but not limited to, the sensitivity of the short circuit protection. |
| − | [[Category:Granity]] | + | It's recommended to set to that which doesn't raise fault flags, and then add 1-2 steps as overhead. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FOV || Over voltage fault threshold || Maximum allowed HV DC bus voltage before entering into over voltage fault. Also defines at which voltage drive starts driving [[Argon user guide/Braking resistor|braking resistor]] to reduce bus voltage.|| See [[Configuring drive voltage limits FUV and FOV]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FUV || Under voltage fault threshold || Minimum allowed HV DC bus voltage before drive starts motor initialization after power-on. Also if this voltage is exceeded during active operation, drive enters into under voltage fault state. || See [[Configuring drive voltage limits FUV and FOV]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Goal deviation faults=== | ||
| + | These settings define how much motor may deviate from the setpoints or allowed operating conditions before entering in fault state. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Short [[GUI]] name !! [[GUI]] name !! Description !! How to use | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FFT || Goal fault filter time || Set time filter for this fault group. Defines how long drive allows exceeding these conditions before entering into fault state. || Normally values between 0-0.5 seconds are safe. Higher value may pose danger to user or equipment as motor is not being stopped soon after error condition. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FPT || Position tracking error threshold || Defines how much position may deviate from the setpoint || rowspan="3" |The value is set as hardware units. Adjust the value and observe the right side value displaying the hardware value converted to a real world units such as ''revolutions/s''. Make sure [[Granity user guide/Machine|Machine tab]] settings are set-up first to get correct conversion. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FVT|| Velocity tracking error threshold ||Defines how much velocity is allowed to deviate from velocity setpoint | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |FEV || Over speed fault || Defines the maximum allowed speed (feedback based) which the axis is allowed to operate before entering to the overspeed fault state | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |FMO || Motion fault threshold|| Defines the sensitivity to enter into motion fault. Used for detecting mechanically blocked motion and DC motor runaway (loss of feedback) || If motion fault feature needed, adjust the value experimentally by increasing it until faults don't occur in normal use. A good starting value may be motor continuous current in milliamperes/2. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |LSF || Limit switch function || Define drive action when position is out of allowed travel range (i.e. limit switch input is open). Device specific notes: | ||
| + | *{{G2.0}}: the ''Dynamic braking'' option is not implemented | ||
| + | *{{G2.1}} and later: LSF also works with software limits (when {{param|HHL}} and {{param|HLL}} are set and homing is successfully finished. With parameter {{param|LFO}} it's possible to control whether soft travel limits will activate the function. | ||
| + | || Choose preferred action when position of motor is beyond allowed travel (i.e. physical limit switches are open). Choices: | ||
| + | *''Do nothing'': no action is taken beyond travel limits (in other words, drive ignores travel limit) | ||
| + | *''Disable torque'': drive will set internal torque setpoint to zero if torque direction is set to cause motor go further from allowed travel direction (in other words, torque is allowed only towards allowed travel direction) | ||
| + | *''Fault stop'': drive sets Motion fault state active which sets drive in inactive state (i.e. motor will be braked and requires user action to move motor back to allowed travel range and then clear fault state) | ||
| + | *''Dynamic braking'': drive attempts to dynamically brake motor (resist motion) if it's being commanded to out of travel bounds but allows command towards allowed direction | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |LSP || Limit switch polarity || Set the polarity of connected limit switch state interpretation | ||
| + | || Choose which digital logic state represents the overtravel condition. As in typical wiring, switch is connected between GND and limit switch input (which has internal pull-up resistor), then following will apply: | ||
| + | *Normally closed (NC) switches, select Logic high when overtravel | ||
| + | *Normally open (NO) switches, select Logic low when overtravel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |LFO || Perform Limit switch function on || Specifies when {{param|LFS}} will activate|| Typical use cases are: | ||
| + | *User has no physical limit switches installed but wishes {{param|LFS}} to activate if motor exceeds the software travel limits {{param|HHL}} or {{param|HLL}}. In this case set this option to "Physical limit switch & Soft travel limits". | ||
| + | *If system has physical limit switches and user also uses software travel limits, then the main travel limiting should be the software limits and physical limits would merely act as backup in case of failure. In this cases it's useful to set this option as "Physical limit switch only". | ||
| + | *If user has only physical limit switches in use and no software travel limits, then this option has no effect. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {{next|[[Granity user guide/Testing]]}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Granity user guide]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pages needing update after FW upgrades]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:24, 19 November 2018
This tab serves as:
- Set fault triggering levels and tolerances
Parameters[edit | edit source]
Drive fault limits[edit | edit source]
| Short GUI name | GUI name | Description | How to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOC | Over current tolerance | Set sensitivity of over current faults | This variable defines how much over current (measured motor phase current above the peak current limit (Machine/MMC) drive allows before entering into fault state. The Minimum setting has lowest threshold and gives fault easier, Maximum tolerates largest over current spikes before faulting.
Set this as low as possible without getting OC faults in normal use to maximally protect your equipment. If larger than Medium setting is needed, see Over current fault troubleshooting for solution to the problem. FOC is firmware specific, it adjust including, but not limited to, the sensitivity of the short circuit protection. It's recommended to set to that which doesn't raise fault flags, and then add 1-2 steps as overhead. |
| FOV | Over voltage fault threshold | Maximum allowed HV DC bus voltage before entering into over voltage fault. Also defines at which voltage drive starts driving braking resistor to reduce bus voltage. | See Configuring drive voltage limits FUV and FOV. |
| FUV | Under voltage fault threshold | Minimum allowed HV DC bus voltage before drive starts motor initialization after power-on. Also if this voltage is exceeded during active operation, drive enters into under voltage fault state. | See Configuring drive voltage limits FUV and FOV. |
Goal deviation faults[edit | edit source]
These settings define how much motor may deviate from the setpoints or allowed operating conditions before entering in fault state.
| Short GUI name | GUI name | Description | How to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFT | Goal fault filter time | Set time filter for this fault group. Defines how long drive allows exceeding these conditions before entering into fault state. | Normally values between 0-0.5 seconds are safe. Higher value may pose danger to user or equipment as motor is not being stopped soon after error condition. |
| FPT | Position tracking error threshold | Defines how much position may deviate from the setpoint | The value is set as hardware units. Adjust the value and observe the right side value displaying the hardware value converted to a real world units such as revolutions/s. Make sure Machine tab settings are set-up first to get correct conversion. |
| FVT | Velocity tracking error threshold | Defines how much velocity is allowed to deviate from velocity setpoint | |
| FEV | Over speed fault | Defines the maximum allowed speed (feedback based) which the axis is allowed to operate before entering to the overspeed fault state | |
| FMO | Motion fault threshold | Defines the sensitivity to enter into motion fault. Used for detecting mechanically blocked motion and DC motor runaway (loss of feedback) | If motion fault feature needed, adjust the value experimentally by increasing it until faults don't occur in normal use. A good starting value may be motor continuous current in milliamperes/2. |
| LSF | Limit switch function | Define drive action when position is out of allowed travel range (i.e. limit switch input is open). Device specific notes:
|
Choose preferred action when position of motor is beyond allowed travel (i.e. physical limit switches are open). Choices:
|
| LSP | Limit switch polarity | Set the polarity of connected limit switch state interpretation | Choose which digital logic state represents the overtravel condition. As in typical wiring, switch is connected between GND and limit switch input (which has internal pull-up resistor), then following will apply:
|
| LFO | Perform Limit switch function on | Specifies when Limit switch functionLFS will activate | Typical use cases are:
|
| Read next |