Difference between revisions of "Configuring cogging torque compensation"
(Created page with "[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cogging_torque Cogging torque] compensation feature in drive that aims to make motor torque production more uniform and ideal. ''"Cogging torq...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 22:50, 2 November 2015
Cogging torque compensation feature in drive that aims to make motor torque production more uniform and ideal.
"Cogging torque of electrical motors is the torque due to the interaction between the permanent magnets of the rotor and the stator slots of a Permanent Magnet (PM) machine. It is also known as detent or ‘no-current’ torque. This torque is position dependent and its periodicity per revolution depends on the number of magnetic poles and the number of teeth on the stator.”
This can be compensated by modulating motor current to counter the motor cogging. In some Granite Devices drives (IONI Pro family on the time of writing) there are options to adjust compensation current by few parameters.
Configuration
Parameters
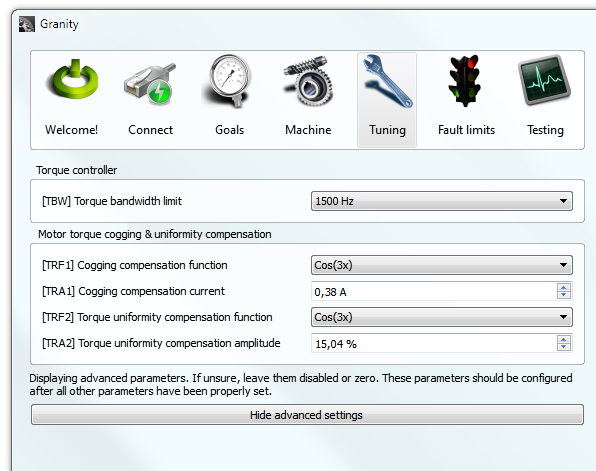
Static no-current cogging compensation is done by summing a fixed amplitude waveform on the torque setpoint. The default waveforms are sinusoidal where phase angle of sine is driven by motor angle.
- Cogging compensation functionTRF1 - selects the function of compensator
- Cogging compensation currentTRA1 - adjusts the amplitude of summed torque command
Dynamic nonuniformity compensation helps to reduce torque ripple when non-zero current is being driven. The method of operation is same, except this time setpoint amplitude is modulated by scaling of torque setpoint instead of summing.
- Torque ripple compensation functionTRF2 - selects the function of compensator
- Torque ripple compensation amplitudeTRA2 - adjust the modulation depth of compensator
Finding values
TODO