Difference between revisions of "Configuring drive voltage limits FUV and FOV"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(tyyli) |
(→How it works) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
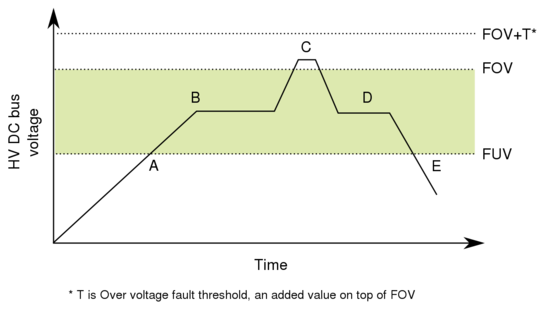
| − | Parameters {{param|FUV}} and {{param|FOV}} define the nominal [[HV DC bus]] voltage range that drive operates in. The purpose of these parameters are to set protect equipment working in a condition where supply voltage is either too low or too high, which is considered a fault condition (see also [[Overvoltage and undervoltage faults]]). FOV also has a special purpose to set a limit where [[regenerative resistor]] will start activating and preventing excessive supply voltage build-up during motor decelerations. | + | [[File:FUV FOV parameters graph.svg|thumb|550px|Typical [[HV DC bus]] voltage waveform and events during normal operation: A) Power-up, drive starts initialization beyond this point, B) normal operation, C) rapid deceleration of motor causing voltage rise, in this region drive attempts to reduce voltage by using [[regenerative resistor]] if present, D) return to nominal voltage range, E) power down.]]Parameters {{param|FUV}} and {{param|FOV}} define the nominal [[HV DC bus]] voltage range that drive operates in. The purpose of these parameters are to set protect equipment working in a condition where supply voltage is either too low or too high, which is considered a fault condition (see also [[Overvoltage and undervoltage faults]]). FOV also has a special purpose to set a limit where [[regenerative resistor]] will start activating and preventing excessive supply voltage build-up during motor decelerations. |
This page guides setting a proper values to FUV and FOV parameters. | This page guides setting a proper values to FUV and FOV parameters. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
=== How it works === | === How it works === | ||
FOV sets the HV DC bus threshold which has following functionality: | FOV sets the HV DC bus threshold which has following functionality: | ||
| − | *If HV DC bus voltage is above | + | *If HV DC bus voltage is above FOV during power-on or restart, drive will not start initialization until the voltage has fallen above the FUV level |
*If voltage is above FOV, drive will start using [[regenerative resistor]] to prevent voltage build up during regeneration | *If voltage is above FOV, drive will start using [[regenerative resistor]] to prevent voltage build up during regeneration | ||
*If voltage is above FOV by a drive specific fixed limit (i.e. ~4.6V on IONI drive or ~25V on Argon), drive will fault into Over voltage fault | *If voltage is above FOV by a drive specific fixed limit (i.e. ~4.6V on IONI drive or ~25V on Argon), drive will fault into Over voltage fault | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Set FOV at least 10% above nominal (15-20% recommended, if possible) HV DC bus voltage after rectification. Nominal HV DC bus voltage can be calculated by formula 1.41*V_AC. Examples: | Set FOV at least 10% above nominal (15-20% recommended, if possible) HV DC bus voltage after rectification. Nominal HV DC bus voltage can be calculated by formula 1.41*V_AC. Examples: | ||
*115 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*115*1.2 = 195 V | *115 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*115*1.2 = 195 V | ||
| − | *230 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*230*1. | + | *230 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*230*1.15 = 374 V |
{{info|If you're using [[Argon]] servo drive, this applies only drives with 2.1.0 or later firmware versions. If you're using older FW, consider upgrading FW or follow the instructions in the subsection below}} | {{info|If you're using [[Argon]] servo drive, this applies only drives with 2.1.0 or later firmware versions. If you're using older FW, consider upgrading FW or follow the instructions in the subsection below}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:50, 4 July 2017
This page guides setting a proper values to FUV and FOV parameters.
Under voltage limit FUV[edit | edit source]
How it works[edit | edit source]
FUV sets the minimum HV DC bus voltage which drive requires to operate.
- If HV DC bus voltage is below FUV during power-on or restart, drive will not start initialization until the voltage has risen above the FUV level
- If HV DC bus voltage drops below FUV during use, drive will fault into Under voltage fault
How to set-up[edit | edit source]
It is recommended to set low enough to allow some supply voltage drop under peak loads but high enough to make drive fault before power supply becomes dangerously overloaded. See guidelines below.
Regulated DC power supplies[edit | edit source]
Set FUV to 90% or at least 1 Volt below PSU's nominal output voltage, whichever is less. Examples:
- 9 VDC regulated PSU - FUV 8 V
- 48 VDC regulated PSU - FUV 43 V
Unregulated DC power supplies[edit | edit source]
These typically may drop voltage more than 20% under high load, it is suggested to set FUV to around 70% of nominal voltage. Examples:
- 50 VDC unregulated PSU - FUV 35V
Mains AC powered drive (such as Argon)[edit | edit source]
It is suggested to set FUV to around 70% of nominal HV DC bus voltage after rectification. Nominal HV DC bus voltage can be calculated by formula 1.41*V_AC. Examples:
- 115 VAC mains - FUV = 1.41*115*0.70 = 114 V
- 230 VAC mains - FUV = 1.41*230*0.70 = 227 V
Over voltage limit FOV[edit | edit source]
How it works[edit | edit source]
FOV sets the HV DC bus threshold which has following functionality:
- If HV DC bus voltage is above FOV during power-on or restart, drive will not start initialization until the voltage has fallen above the FUV level
- If voltage is above FOV, drive will start using regenerative resistor to prevent voltage build up during regeneration
- If voltage is above FOV by a drive specific fixed limit (i.e. ~4.6V on IONI drive or ~25V on Argon), drive will fault into Over voltage fault
How to set-up[edit | edit source]
It is recommended to set FOV high enough to allow some supply voltage increase during motor decelerations and to allow normal voltage fluctuations of power source. Guidelines as starting point:
Regulated DC power supplies[edit | edit source]
Set FOV only little bit above the nominal voltage, however at least 3%. Examples
- 48 VDC regulated PSU - FOV 49.5 V
Unregulated DC power supplies[edit | edit source]
Set FOV at least 12% above nominal voltage because AC input voltage fluctuations will also change output voltage of the PSU. Examples:
- 50 VDC unregulated PSU - FOV 56 V
Mains AC powered drive (such as Argon)[edit | edit source]
Set FOV at least 10% above nominal (15-20% recommended, if possible) HV DC bus voltage after rectification. Nominal HV DC bus voltage can be calculated by formula 1.41*V_AC. Examples:
- 115 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*115*1.2 = 195 V
- 230 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*230*1.15 = 374 V
| If you're using Argon servo drive, this applies only drives with 2.1.0 or later firmware versions. If you're using older FW, consider upgrading FW or follow the instructions in the subsection below |
Set-up of FOV on Argon with firmware 2.0.0 or earlier[edit | edit source]
FOV parameter works differently on Argon firmware 2.0 and earlier (including 1.x series). On these versions the FOV sets the fault threshold voltage and activation of regenerative resistor happens when HV DC bus voltage rises above 91% of FUV. Because of these differences, it is necessary to set value the following way:
- 115 VAC mains - FOV = 1.41*115*1.2/0.91 = 213 V
- 230 VAC mains - FOV = maximum settable value
| Setting FOV too low on outdated firmwares may cause regenerative resistor heating whenever power is on. |