Difference between revisions of "Motor types"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(→Comparison) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| Rated torque vs size || High || Low || Medium || Medium | | Rated torque vs size || High || Low || Medium || Medium | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Dynamic performance || Low, medium || Medium||High|| | + | | Dynamic performance || Low, medium || Medium||High||High |
|- | |- | ||
| Motion smoothness || Low to high||Medium||Medium||High | | Motion smoothness || Low to high||Medium||Medium||High | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| Energy efficiency || Low, medium || Medium || High || High | | Energy efficiency || Low, medium || Medium || High || High | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Feedback devices]] | *[[Feedback devices]] | ||
[[Category:Hardware]] | [[Category:Hardware]] | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 18 April 2012
Position, velocity and torque/force control applications mainly rely on two main categories of motors: servo motors and stepping motors.
Servo motor is a electromechanical mechanical actuator with feedback allowing precision closed loop motion control and monitoring.
Stepping motor is a low cost alternative to servo motors and can be operated without feedback devices.
Contents
Construction
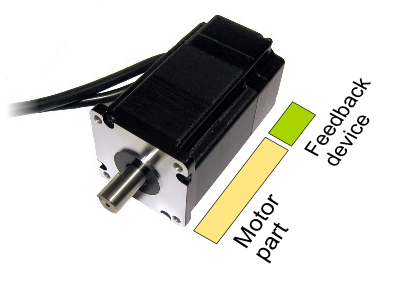
Servo motor consists two main parts:
- Motor part - typically electromagnetic device that produces torque or force when driven with current
- Feedback device - typically electronic device that outputs measurement information such as shaft angle or velocity
Stepping motors can be used without any feedback device.
Shapes
Motors and feedback devices come mainly in two shapes:
- Rotary
- Linear
Shape of motor doesn't change their electromechanical principle so both types of motors can be driven with same drives.
Motor technologies
List of electromagnetic motor part types.
AC
Typical AC (alternating current) servo motor is a 3 phase permanent magnet syncronous machine. This type of motors are driven by 3 wires each driving one phase coil. In ideal case 3 phase AC servo is driven by sinusoidal current waveforms that are synchronized to the permanent magnet rotor.
BLDC
BLDC (brushless DC) is very similar to AC motor with only expection that it is desgined to be driven by trapezoidal current waveforms instead of sinusoidal. BLDC motors can always be driven with same drives regardless of current waveform matching.
Brush DC
Brush DC (direct current) motors typically have permanent magnet stator and rotor with mechanical commutator with brushes.
Stepping motor
Stepper motors are high pole count permanent magnet brushless motors with 2 or 3 phase windings. High pole count enables position control without feedback devices but with several drawbacks such as risk of lost position.
Comparison
Comparison of motor technologies
| Stepping motor | DC servo | BLDC servo | AC servo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed loop | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Torque control | No, inpractical | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Velocity control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Position control | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Available speed range | Low, Medium | Medium | High | Highest |
| Rated torque vs size | High | Low | Medium | Medium |
| Dynamic performance | Low, medium | Medium | High | High |
| Motion smoothness | Low to high | Medium | Medium | High |
| Endurance | High | Medium | High | High |
| Energy efficiency | Low, medium | Medium | High | High |