Difference between revisions of "Argon user guide/J5 connector electrical interfacing"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
(→Complete example with pulse & direction) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
[[file:j5pulsedircomplete.png|700px]] | [[file:j5pulsedircomplete.png|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
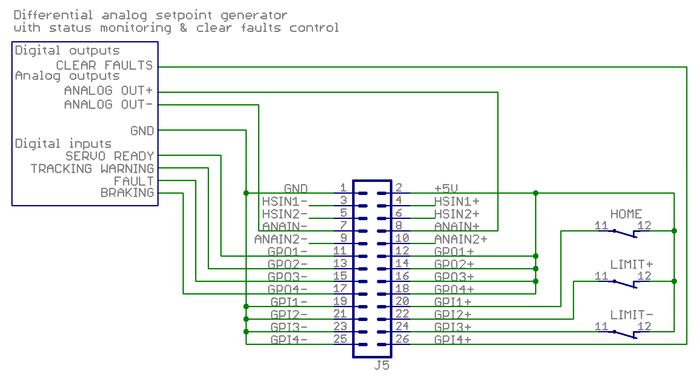
| + | ===Complete example with differential analog setpoint=== | ||
| + | Same as above expect this time setpoint signal is a differential analog voltage output. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:j5analogcomplete.png|700px]] | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 17 August 2013
This article explains the internal circuity behind J5 connector of Argon servo drive.| Exceeding ratings may affect drive operation and cause instability or even damage the drive. |
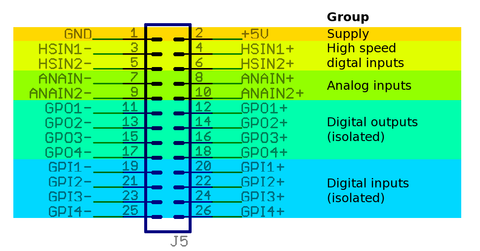
J5 connector pin-out and electrical ratings
- Pin-out: Argon wiring
- Electrical specifications: Argon specifications
Pin groups
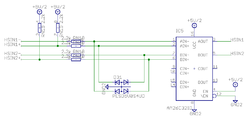
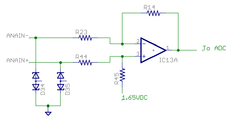
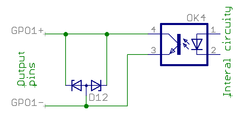
Internal schematics of pin groups
These images show the circuity behind the J5 connector inside the Argon drive (simplified schematics). Left side end represents J5 pins and right side continues to drive internal circuity.
Supply
Supply pins output a regulated 5V voltage to external circuits. GND pin is tied to J3 connector V- terminal.
- Electrical properties
- Output voltage 4.9-5.2 V
- Maximum load 500 mA
- Maximum injected current -10 mA
| Never connect multiple supply outputs parallel. Supply output may be connected only current consuming circuity to prevent current injection to the supply port. |
High speed digital input group
HSIN is differential digital input capable of receiving digital signals up to 4 MHz.
Electrical properties
- Maximum voltage to HSINx+/- pins referenced to GND: -0.5 to 6V. Nominal 3.3 or 5.0V.
- Maximum injected current +/- 10 mA
- When negative input (HSINx-) is left floating, it floats around 2.5V
- Input state reads logic 1 when voltage on positive pin is greater than voltage on negative pin, otherwise it's logic 0
Wiring when driving using differential source
- Positive outputs of source to HSINx+
- Negative outputs of source to HSINx-
- GND must be connected to source ground
Wiring when driving using single ended source (TTL, CMOS or open collector)
- Outputs of source to HSINx+
- Leave HSINx- floating
- GND must be connected to source ground
Analog input group
Analog input accepts ±10V from and may be used as setpoint signal. Electrical properties
- Input impedance ~10 kΩ
- Maximum ANAINx+/- pin voltage vs GND ±20V
- Maximum injected current ±10 mA
- Sampling resolution 12 bits
Wiring to differential signal source
- Connect positive output to ANAINx+
- Connect negative (inverted) output to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
Wiring to single ended signal source
- Connect output to ANAINx+
- Connect source ground to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
Digital output group
Digital output is an optoisolated transistor output to drive various types of inputs of target devices (logic gates, relays, lights etc) Electrical properties
- Load voltage range 3-24V
- Maximum allowed load 50 mA
- Logic 1 state equals conducting state of optocoupler transistor (current flows from GPO+ to GPO- pins), logic 0 stops current flow between GPO+ to GPO- pins.
- + to - pin voltage drop at 50 mA less than 2 VDC
Wiring to logic gate input (CMOS or TTL)
- Connect GPO+ pin to target VCC (typ 5V)
- Connect GPO- pin to target input pin (so input pin is pulled to 5V when output state is logic 1)
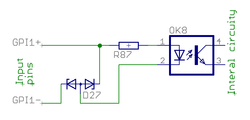
Digital input group
Digital inputs are optoisolated (floating potential) inputs for general purpose control signals. Electrical properties
- Signal voltage range 3-24V
- Logic 0 when difference between +/- inputs less than 1.5V, logic 1 when voltage is between 2.9-25V
- Current needed to drive logic 1 is 0.8-9 mA depending on input voltage
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs 27 VDC
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs vs GND 120 VDC
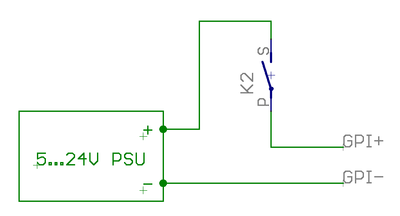
Connection to electromechanical switch or relay
- See schematics image in right side
Connection to CMOS source
- Connect source output to GPIx+ input
- Connect source ground to GPIx- input
Connection to open collector or TTL source
- Connect source output to GPIx- input
- Connect source VCC (typ 5V) to GPOx+ input
| Digital input and output isolation is only functional and does not provide safety insulation. Connect only to ELV circuits. |
Examples
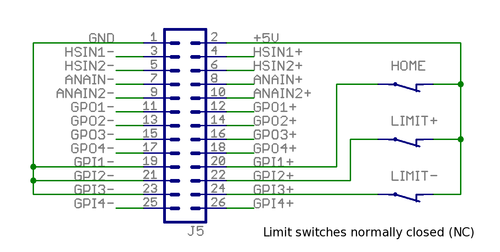
Wiring axis limit and home switches to J5
To operate the motor, limit switches must be connected to the GPI1 and GPI2. Feeding logic 1 to one of these ports enables axis motion feed in certain direction.
The behavior of feed enable signals can be configured via Granity machine tab. Logic 1 to these pins is required for drive operation:
- GPI1 - enable positive direction feed.
- GPI2 - enable negative direction feed.
Home switch (optional):
- GPI3 - home switch input. Polarity can be configured via Granity.
In the image below A way to connect switches to J5 port. Inputs are supplied by the J5 connector 5V output. Alternatively the switches may be also supplied from an external 5-24VDC supply.
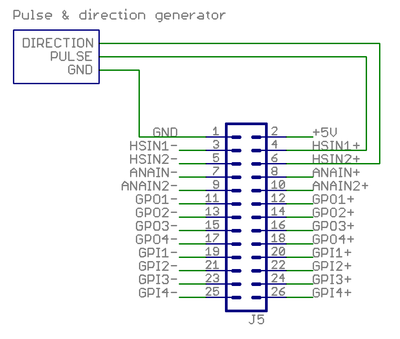
Pulse and direction setpoint
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended pulse and direction controller.
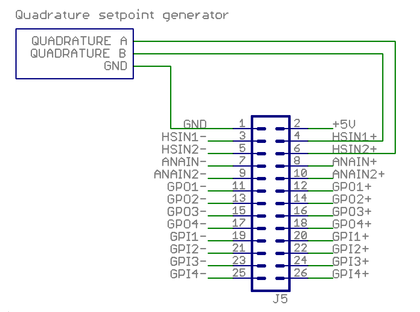
Quadrature signal setpoint
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended quadrature controller.
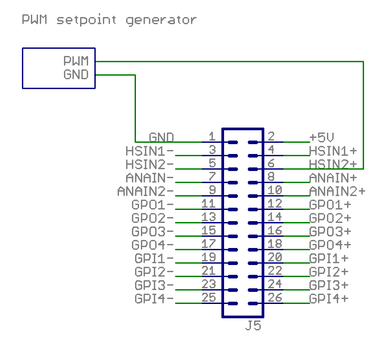
PWM signal setpoing
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended PWM controller.
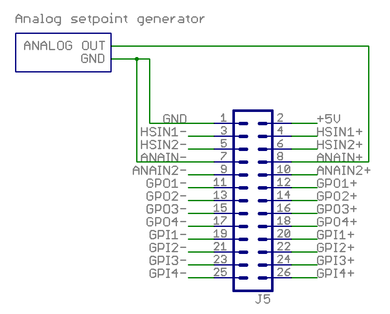
Analog signal setpoint
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended Analog setpoint controller. Maximum analog signal voltage is +/-10V.
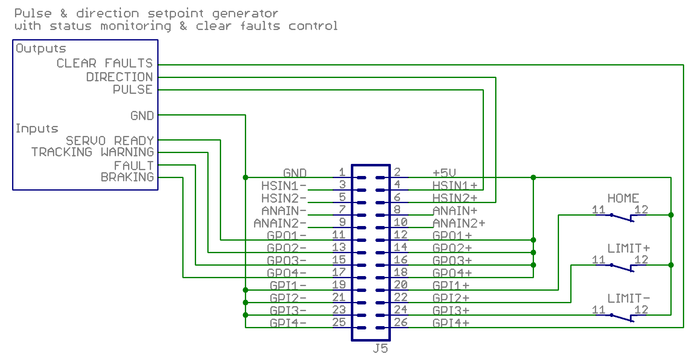
Complete example with pulse & direction
The examples above can be combined to achieve the user goals. The example below has complete set of I/O features used.
- Pulse & direction set point
- Clear faults output (off-on-off pulse generated by controller user if FAULT input goes on)
- Monitoring of drive state: servo ready, tracking error warning, drive fault, motor braking status
- Axis limit switches & home switch
Notes:
- The controller in the example has 5 volt single ended inputs & outputs
- Controller inputs have pull-down resistor or other means to ensure off or 0 state when input is floating
- It's not required to to monitor & control the I/O lines at controller
Complete example with differential analog setpoint
Same as above expect this time setpoint signal is a differential analog voltage output.