Difference between revisions of "Argon user guide/J5 connector electrical interfacing"
From Granite Devices Knowledge Wiki
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{damage|Exceeding ratings may affect drive operation and cause instability or even damage the drive.}} | {{damage|Exceeding ratings may affect drive operation and cause instability or even damage the drive.}} | ||
| − | == | + | ==J5 connector pin-out and electrical ratings== |
| − | + | *Pin-out: [[Argon wiring]] | |
| − | ==Pin | + | *Electrical specifications: [[Argon specifications]] |
| + | ==Pin groups== | ||
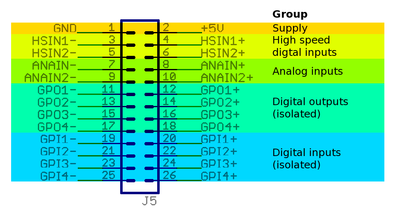
| + | [[File:J5groups.png|thumbnail|J5 connector pin groups]] | ||
===Supply=== | ===Supply=== | ||
Supply pins output a regulated 5V voltage to external circuits. GND pin is tied to J3 connector V- terminal. | Supply pins output a regulated 5V voltage to external circuits. GND pin is tied to J3 connector V- terminal. | ||
Revision as of 11:48, 17 August 2013
This article explains the internal circuity behind J5 connector of Argon servo drive.| Exceeding ratings may affect drive operation and cause instability or even damage the drive. |
J5 connector pin-out and electrical ratings
- Pin-out: Argon wiring
- Electrical specifications: Argon specifications
Pin groups
Supply
Supply pins output a regulated 5V voltage to external circuits. GND pin is tied to J3 connector V- terminal.
- Electrical properties
- Output voltage 4.9-5.2 V
- Maximum load 500 mA
- Maximum injected current -10 mA
| Never connect multiple supply outputs parallel. Supply output may be connected only current consuming circuity to prevent current injection to the supply port. |
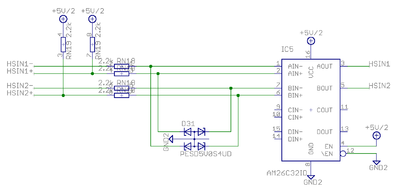
High speed digital input
HSIN is differential digital input capable of receiving digital signals up to 4 MHz.
- Electrical properties
- Maximum voltage to HSINx+/- pins referenced to GND: -0.5 to 6V. Nominal 3.3 or 5.0V.
- Maximum injected current +/- 10 mA
- When negative input (HSINx-) is left floating, it floats around 2.5V
- Input state is logic 1 when voltage on positive pin is greater than voltage on negative pin, otherwise it's logic 0
- Wiring when driving using differential source
- Positive outputs of source to HSINx+
- Negative outputs of source to HSINx-
- GND must be connected to source ground
- Wiring when driving using single ended source (TTL, CMOS or open collector)
- Outputs of source to HSINx+
- Leave HSINx- floating
- GND must be connected to source ground
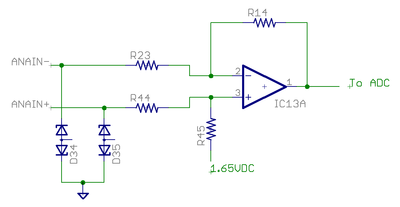
Analog input
Analog input accepts ±10V from and may be used as setpoint signal.
- Electrical properties
- Input impedance ~10 kΩ
- Maximum ANAINx+/- pin voltage vs GND ±20V
- Maximum injected current ±10 mA
- Sampling resolution 12 bits
- Wiring to differential signal source
- Connect positive output to ANAINx+
- Connect negative (inverted) output to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
- Wiring to single ended signal source
- Connect output to ANAINx+
- Connect source ground to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
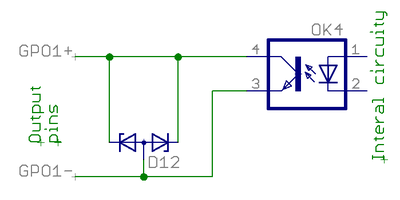
Digital output
Digital output is an optoisolated transistor output to drive various types of inputs of target devices (logic gates, relays, lights etc)
- Electrical properties
- Load voltage range 3-24V
- Maximum allowed load 50 mA
- Logic 1 state equals conducting state of optocoupler transistor (current flows from GPO+ to GPO- pins), logic 0 stops current flow between GPO+ to GPO- pins.
- + to - pin voltage drop at 50 mA less than 2 VDC
- Wiring to logic gate input (CMOS or TTL)
- Connect GPO+ pin to target VCC (typ 5V)
- Connect GPO- pin to target input pin (so input pin is pulled to 5V when output state is logic 1)
| Digital output isolation is only functional and does not provide safety insulation. Connect only to ELV circuits. |
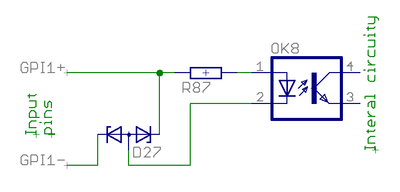
Digital input
Digital inputs are optoisolated (floating potential) inputs for general purpose control signals.
- Electrical properties
- Signal voltage range 3-24V
- Logic 0 when difference between +/- inputs less than 1.5V, logic 0 when more than 2.9V
- Current needed to drive logic 1 is 0.8-9 mA depending on input voltage
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs 27 VDC
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs vs GND 120 VDC
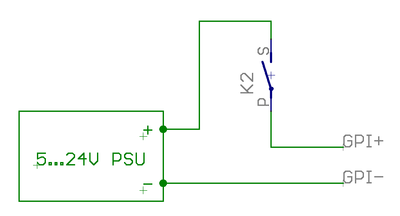
- Connection to electromechanical switch or relay
- See schematics image in right side
- Connection to CMOS source
- Connect source output to GPIx+ input
- Connect source ground to GPIx- input
- Connection to open collector or TTL source
- Connect source output to GPIx- input
- Connect source VCC (typ 5V) to GPOx+ input
| Digital input isolation is only functional and does not provide safety insulation. Connect only to ELV circuits. |
Example 1
This example shows how to wire J5 for typical pulse and direction control.
TODO