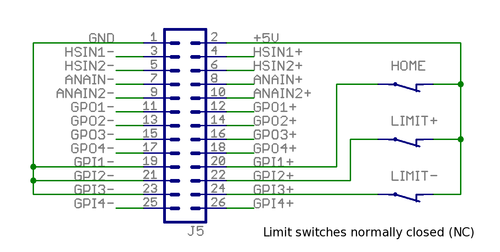
Argon J5 connector wiring
| Exceeding ratings may affect drive operation and cause instability or even damage the drive. |
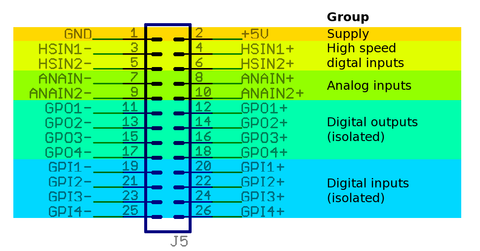
J5 connector pin-out and electrical ratings[edit | edit source]
- Overview: Argon wiring
- I/O electrical ratings: Argon specifications
Pin groups[edit | edit source]
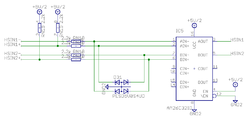
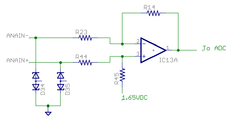
Internal schematics of pin groups[edit | edit source]
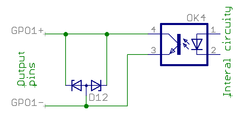
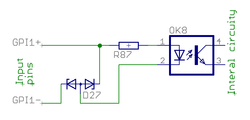
These images show the circuity behind the J5 connector inside the Argon drive (simplified schematics). Left side end represents J5 pins and right side continues to drive internal circuity.
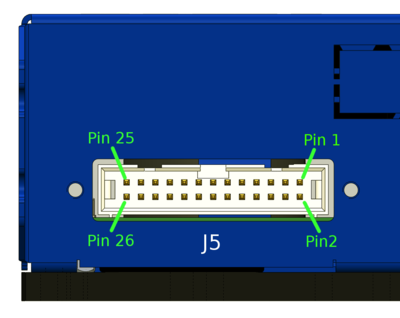
Pin-out[edit | edit source]
| Pin # | Pin name | Electrical | Isolated | Function¹ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Supply | No² | Ground |
| 2 | +5V_OUT | Supply | 5V output | |
| 3 | HSIN1- | High speed digital input |
| |
| 4 | HSIN1+ | High speed digital input | ||
| 5 | HSIN2- | High speed digital input |
| |
| 6 | HSIN2+ | High speed digital input | ||
| 7 | ANAIN1- | Analog input | Analog input setpoint | |
| 8 | ANAIN1+ | Analog input | ||
| 9 | ANAIN2- | Analog input | Direction reversal signal for analog input setpoint signal. | |
| 10 | ANAIN2+ | Analog input | ||
| 11 | GPO1- | Digital output | Yes² | Servo ready status. True when drive is initialized and ready to accept user commands/setpoint. |
| 12 | GPO1+ | Digital output | ||
| 13 | GPO2- | Digital output | Position/velocity control mode tracking error warning status. True when tracking error has reached more than user configured 1/8 of fault limit value or when drive is not enabled. May be used by controller to throttle the setpoint thus avoid triggering an tracking error fault. May require FW upgrade. | |
| 14 | GPO2+ | Digital output | ||
| 15 | GPO3- | Digital output | Fault stop status. True when drive is stopped due to fault. | |
| 16 | GPO3+ | Digital output | ||
| 17 | GPO4- | Digital output | Braking status. Set true when drive attempts to brake motor. | |
| 18 | GPO4+ | Digital output | ||
| 19 | GPI1- | Digital input | Home switch input. | |
| 20 | GPI1+ | Digital input | ||
| 21 | GPI2- | Digital input | Positive feed enable input. Used for axis limit switches. | |
| 22 | GPI2+ | Digital input | ||
| 23 | GPI3- | Digital input | Negative feed enable input. Used for axis limit switches. | |
| 24 | GPI3+ | Digital input | ||
| 25 | GPI4- | Digital input | Clear drive faults input. Transition from false to true attempts to reset active faults of drive. If drive is simultaneously in enabled state, motor will start moving immediately. | |
| 26 | GPI4+ | Digital input |
¹) This is the default function with stock firmware. Function may be different in future or custom firmware versions.
²) Non-isolated lines are referenced to GND pin / J3 V- terminal. Isolated lines have functional isolation between GND and other isolated +-/- pairs.
Wiring guide[edit | edit source]
Supply[edit | edit source]
Supply pins output a regulated 5V voltage to external circuits. GND pin is tied to J3 connector V- terminal.
- Electrical properties
- Output voltage 4.9-5.2 V
- Maximum load 500 mA
- Maximum injected current -10 mA
| Never connect multiple supply outputs parallel. Supply output may be connected only current consuming circuity to prevent current injection to the supply port. |
High speed digital input group[edit | edit source]
HSIN is differential digital input capable of receiving digital signals up to 4 MHz.
Electrical properties
- Maximum voltage to HSINx+/- pins referenced to GND: -0.5 to 6V. Nominal 3.3 or 5.0V.
- Maximum injected current +/- 10 mA
- When negative input (HSINx-) is left floating, it floats around 2.5V
- Input state reads logic 1 when voltage on positive pin is greater than voltage on negative pin, otherwise it's logic 0
Wiring when driving using differential source
- Positive outputs of source to HSINx+
- Negative outputs of source to HSINx-
- GND must be connected to source ground
Wiring when driving using single ended source (TTL, CMOS or open collector)
- Outputs of source to HSINx+
- Leave HSINx- floating
- GND must be connected to source ground
Analog input group[edit | edit source]
Analog input accepts ±10V from and may be used as setpoint signal. Electrical properties
- Input impedance ~10 kΩ
- Maximum ANAINx+/- pin voltage vs GND ±25V
- Maximum injected current ±10 mA
- Sampling resolution 12 bits
Wiring to differential signal source
- Connect positive output to ANAINx+
- Connect negative (inverted) output to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
Wiring to single ended signal source
- Connect output to ANAINx+
- Connect source ground to ANAINx-
- Connect source ground to GND
Wiring to 0-10V analog output with digital direction output:
- Follow the earlier guidelines but connect controller's direction signal to ANAIN2+ and the ground reference of digital output to ANAIN2-. Setpoint gets inverted inside the drive if ANAIN2 voltage is between 3-24VDC and non-inverted between 0-3VDC. May require FW upgrade.
Digital output group[edit | edit source]
Digital output is an optoisolated transistor output to drive various types of inputs of target devices (logic gates, relays, lights etc) Electrical properties
- Load voltage range 3-24V
- Maximum allowed load 50 mA
- Logic 1 state equals conducting state of optocoupler transistor (current flows from GPO+ to GPO- pins), logic 0 stops current flow between GPO+ to GPO- pins.
- + to - pin voltage drop at 50 mA less than 2 VDC
Wiring to logic gate input (CMOS or TTL)
- Connect GPO+ pin to target VCC (typ 5V)
- Connect GPO- pin to target input pin (so input pin is pulled to 5V when output state is logic 1)
| Multiple GPO's may be wired parallel to combine multiple status signals into one wire. In such connection the combined output becomes logic 1 (conductive) if any of the paralleled outputs becomes logic 1. |
Digital input group[edit | edit source]
Digital inputs are optoisolated (floating potential) inputs for general purpose control signals. Electrical properties
- Signal voltage range 3-24V
- Logic 0 when difference between +/- inputs less than 1.5V, logic 1 when voltage is between 2.9-25V
- Current needed to drive logic 1 is 0.8-9 mA depending on input voltage
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs 27 VDC
- Maximum voltage difference between GPIx+/- inputs vs GND 120 VDC
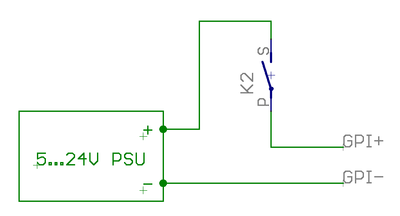
Connection to electromechanical switch or relay
- See schematics image in right side
Connection to CMOS source
- Connect source output to GPIx+ input
- Connect source ground to GPIx- input
Connection to open collector or TTL source
- Connect source output to GPIx- input
- Connect source VCC (typ 5V) to GPOx+ input
| Digital input and output isolation is only functional and does not provide safety insulation. Connect only to ELV circuits. |
Examples[edit | edit source]
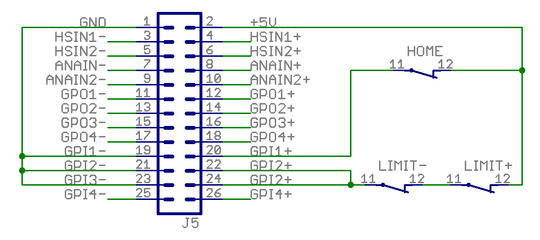
Wiring axis limit and home switches to J5[edit | edit source]
To operate the motor, limit switches must be connected to the GPI1 and GPI2. Feeding logic 1 to one of these ports enables axis motion feed in certain direction.
The behavior of feed enable signals can be configured via Granity machine tab. Logic 1 to these pins is required for drive operation:
- GPI1 - enable positive direction feed.
- GPI2 - enable negative direction feed.
Home switch (optional):
- GPI3 - home switch input. Polarity can be configured via Granity.
In the image below A way to connect switches to J5 port. Inputs are supplied by the J5 connector 5V output. Alternatively the switches may be also supplied from an external 5-24VDC supply.
The example below illustrates an alternative way of connecting limit switches that are connected in series. However this way requires that axis is being manually pulled away from end of travel if either switch is open as drive doesn't know which way is the safe running direction.
Alternative limit switch wiring considerations[edit | edit source]
It is possible to connect limit switches several way, or omit them completely. The table below summarizes the different methods:
| Method # | Connections / configurations | End of travel causes a fault stop state | End of travel causes active braking of motor | Can move motor electrically out end of travel | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Connect limit switches independently to GPI2 and GPI3 inputs | Yes (but depends on parameterization) | Yes (but depends on parameterization) | Yes | This is the most typical method used |
| B | Connect limit switches in series to GPI2 and GPI3 inputs parallel | Yes (but depends on parameterization) | Yes (but depends on parameterization) | No | Drive has info only that limit switch is open but no info about which way is safe to move |
| C | No limit switches, instead use homing function (position control mode only) and set soft travel limits by parameterization | No | Yes | Yes | Sensorless & wireless solution |
| D | Connect limit switches Safe torque off input | Yes | No, motor may free wheel | No | A very secure way to remove torque from motor. If such feature is desired, it's recommended to install second pair of limit switches or use soft travel limits that stop motion before the STO switches, so STO switches would serve only as backup. |
| E | Connect limit switch to enable drive input | No | Yes | Yes |
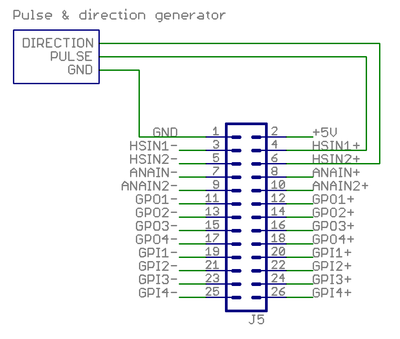
Pulse and direction setpoint[edit | edit source]
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended pulse and direction controller.
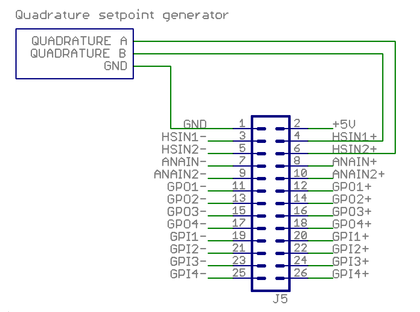
Quadrature signal setpoint[edit | edit source]
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended quadrature controller.
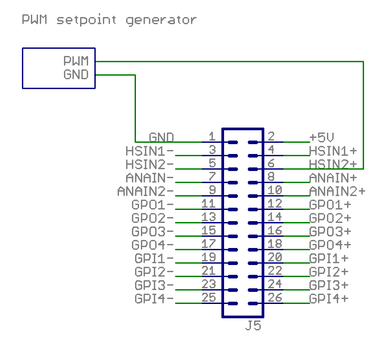
PWM signal setpoing[edit | edit source]
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended PWM controller.
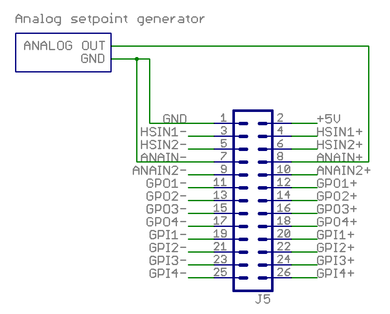
Analog signal setpoint[edit | edit source]
This example shows how to wire a typical single ended Analog setpoint controller. Maximum analog signal voltage is +/-10V.
0-10V analog input with digital direction signal[edit | edit source]
Follow the earlier guidelines but connect controller's direction signal to ANAIN2+ and the ground reference of digital output to ANAIN2-. Setpoint gets inverted inside the drive if ANAIN2 voltage is between 3-24VDC and non-inverted between 0-3VDC. May require FW upgrade.
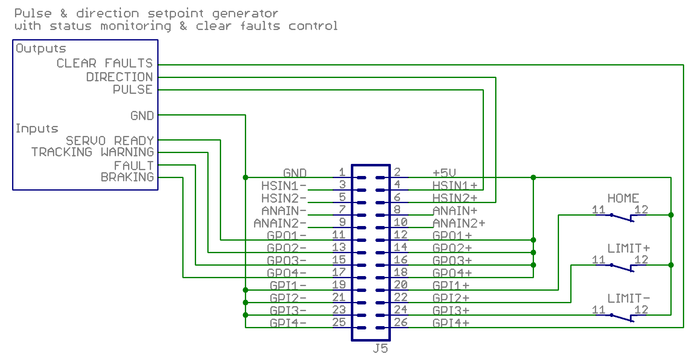
Complete example with pulse & direction[edit | edit source]
The examples above can be combined to achieve the user goals. The example below has complete set of I/O features used.
- Pulse & direction set point
- Clear faults output (off-on-off pulse generated by controller user if FAULT input goes on)
- Monitoring of drive state: servo ready, tracking error warning, drive fault, motor braking status
- Axis limit switches & home switch
Notes:
- The controller in the example has 5 volt single ended inputs & outputs
- Controller inputs have pull-down resistor or other means to ensure off or 0 state when input is floating
- It's not required to to monitor & control the I/O lines at controller
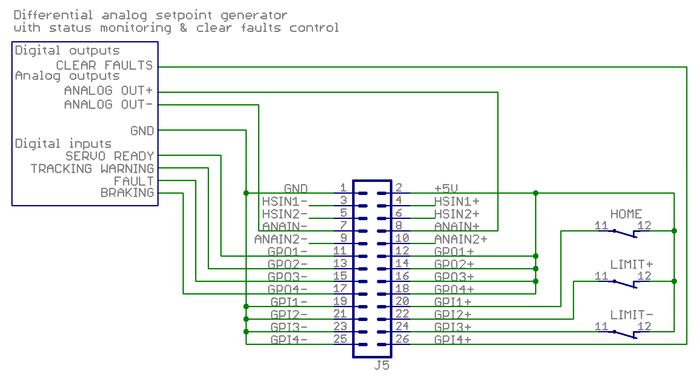
Complete example with differential analog setpoint[edit | edit source]
Same as above expect this time the setpoint signal is a differential analog voltage output (max +/-10V).
In no event the Product Information or parts hereof shall be regarded as guarantee of conditions or characteristics. The Product Information or any part thereof may also not be regarded as a warranty of any kind. No liability of any kind shall be assumed by Author with respect to Product Information or any use made by you thereof, nor shall Author indemnify you against or be liable for any third party claims with respect to such information or any use thereof.
As content of this Wiki may be edited by user community, Granite Devices Oy or it's affiliates do not take any responsibility of the contents of this Wiki. Use information at your own risk. However, Granite Devices staff attempts to review all changes made to this Wiki and keep information trustworthy.
Without written consent, Granite Devices' Products or Intellectual Property shall not be used in situations or installations where living beings, material property, or immaterial property could be harmed by the operation, features or failures of Product. Products may only be used in a way where hazards like moving parts, electric shock, laser radiation, or fire can't be realized even if the content of this Wiki would suggest otherwise.